Human embryonic and rat adult stem cells with primitive endoderm-like phenotype can be fated to definitive endoderm, and finally hepatocyte-like cells
- PMID: 20711405
- PMCID: PMC2920330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012101
Human embryonic and rat adult stem cells with primitive endoderm-like phenotype can be fated to definitive endoderm, and finally hepatocyte-like cells
Abstract
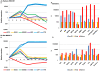
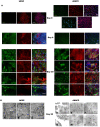
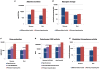
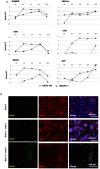
Stem cell-derived hepatocytes may be an alternative cell source to treat liver diseases or to be used for pharmacological purposes. We developed a protocol that mimics mammalian liver development, to differentiate cells with pluripotent characteristics to hepatocyte-like cells. The protocol supports the stepwise differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (ESC) to cells with characteristics of primitive streak (PS)/mesendoderm (ME)/definitive endoderm (DE), hepatoblasts, and finally cells with phenotypic and functional characteristics of hepatocytes. Remarkably, the same protocol can also differentiate rat multipotent adult progenitor cells (rMAPCs) to hepatocyte-like cells, even though rMAPC are isolated clonally from cultured rat bone marrow (BM) and have characteristics of primitive endoderm cells. A fraction of rMAPCs can be fated to cells expressing genes consistent with a PS/ME/DE phenotype, preceding the acquisition of phenotypic and functional characteristics of hepatocytes. Although the hepatocyte-like progeny derived from both cell types is mixed, between 10-20% of cells are developmentally consistent with late fetal hepatocytes that have attained synthetic, storage and detoxifying functions near those of adult hepatocytes. This differentiation protocol will be useful for generating hepatocyte-like cells from rodent and human stem cells, and to gain insight into the early stages of liver development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Gómez-Lechón MJ, Castell JV, Donato MT. An update on metabolism studies using human hepatocytes in primary culture. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2008;4:837–854. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura M, Koeda A, Suganuma Y, Suzuki E, Shimizu T, et al. Comparison of inducibility of CYP1A and CYP3A mRNAs by prototypical inducers in primary cultures of human, cynomolgus monkey, and rat hepatocytes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2007;22:178–186. - PubMed
-
- Dhawan A, Mitry RR, Hughes RD. Hepatocyte transplantation for liver-based metabolic disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006;29:431–435. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RA, Strom SC. Human Hepatocyte Transplantation: Worldwide Results. Transplantation. 2006;82:441–449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

