Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1) contributes to high NaCl-induced activation of the osmoprotective transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP
- PMID: 20711462
- PMCID: PMC2920327
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012108
Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1) contributes to high NaCl-induced activation of the osmoprotective transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP
Abstract
Background: Hypertonicity, such as induced by high NaCl, increases the activity of the transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP whose target genes increase osmoprotective organic osmolytes and heat shock proteins.
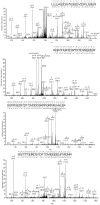
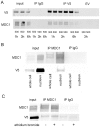
Methodology: We used mass spectrometry to analyze proteins that coimmunoprecipitate with TonEBP/OREBP in order to identify ones that might contribute to its high NaCl-induced activation.
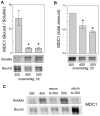
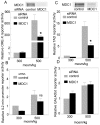
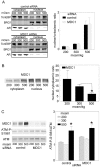
Principal findings: We identified 20 unique peptides from Mediator of DNA Damage Checkpoint 1 (MDC1) with high probability. The identification was confirmed by Western analysis. We used small interfering RNA knockdown of MDC1 to characterize its osmotic function. Knocking down MDC1 reduces high NaCl-induced increases in TonEBP/OREBP transcriptional and transactivating activity, but has no significant effect on its nuclear localization. We confirm six previously known phosphorylation sites in MDC1, but do not find evidence that high NaCl increases phosphorylation of MDC1. It is suggestive that MDC1 acts as a DNA damage response protein since hypertonicity reversibly increases DNA breaks, and other DNA damage response proteins, like ATM, also associate with TonEBP/OREBP and contribute to its activation by hypertonicity.
Conclusions/significance: MDC1 associates with TonEBP/OREBP and contributes to high NaCl-induced increase of that factor's transcriptional activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated, a DNA damage-inducible kinase, contributes to high NaCl-induced nuclear localization of transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Sep;289(3):F506-11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00417.2004. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15840767
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates activation of ATM by high NaCl and by ionizing radiation: Role in osmoprotective transcriptional regulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 6;103(23):8882-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602911103. Epub 2006 May 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16728507 Free PMC article.
-
ATM, a DNA damage-inducible kinase, contributes to activation by high NaCl of the transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 8;101(23):8809-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403062101. Epub 2004 Jun 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15173573 Free PMC article.
-
The complex matter of DNA double-strand break detection.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):40-4. doi: 10.1042/bst0310040. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546650 Review.
-
Tonicity-dependent regulation of osmoprotective genes in mammalian cells.Contrib Nephrol. 2006;152:125-141. doi: 10.1159/000096320. Contrib Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 17065809 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Inflammatory Functions of Macrophages and T Lymphocytes by NFAT5.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 20;10:535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00535. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30949179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFAT5 in cellular adaptation to hypertonic stress - regulations and functional significance.J Mol Signal. 2013 Apr 23;8(1):5. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-8-5. J Mol Signal. 2013. PMID: 23618372 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed transcripts and associated protein pathways in basilar artery smooth muscle cells of the high-salt intake-induced hypertensive rat.PeerJ. 2020 Oct 13;8:e9849. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9849. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33083107 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cell-specific targets of sumoylation during mouse spermatogenesis.Reproduction. 2016 Feb;151(2):149-66. doi: 10.1530/REP-15-0239. Reproduction. 2016. PMID: 26701181 Free PMC article.
-
High NaCl-induced activation of CDK5 increases phosphorylation of the osmoprotective transcription factor TonEBP/OREBP at threonine 135, which contributes to its rapid nuclear localization.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Mar 1;22(5):703-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-08-0681. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21209322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagnasco S, Balaban R, Fales HM, Yang YM, Burg M. Predominant osmotically active organic solutes in rat and rabbit renal medullas. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:5872–5877. - PubMed
-
- Rauchman MI, Pullman J, Gullans SR. Induction of molecular chaperones by hyperosmotic stress in mouse inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:F9–17. - PubMed
-
- Ko BC, Turck CW, Lee KW, Yang Y, Chung SS. Purification, identification, and characterization of an osmotic response element binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;270:52–61. - PubMed
-
- Burg MB, Ferraris JD, Dmitrieva NI. Cellular response to hyperosmotic stresses. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:1441–1474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

