Type 2 diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for the onset of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 20711716
- PMCID: PMC2974923
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-010-1874-x
Type 2 diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for the onset of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: An earlier meta-analysis showed that diabetes is a risk factor for the development and/or recurrence of depression. Yet whether this risk is different for studies using questionnaires than for those relying on diagnostic criteria for depression has not been examined. This study examined the association of diabetes and the onset of depression by reviewing the literature and conducting a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies on this topic.
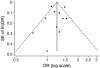
Methods: EMBASE, MEDLINE and PsycInfo were searched for articles published up to September 2009. All studies that examined the relationship between type 2 diabetes and the onset of depression were included. Pooled relative risks were calculated using fixed and random effects models.
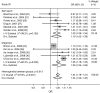
Results: Eleven studies met our inclusion criteria for this meta-analysis. Based on the pooled data, including 48,808 cases of type 2 diabetes without depression at baseline, the pooled relative risk was 1.24 (95% CI 1.09-1.40) for the random effects model. This risk was significantly higher for studies relying on diagnostic criteria of depression than for studies using questionnaires. However, this difference was no longer significant when controlled for year of publication.
Conclusions/interpretation: Compared with non-diabetic controls, people with type 2 diabetes have a 24% increased risk of developing depression. The mechanisms underlying this relationship are still unclear and warrant further research.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

