Systematic analysis of helical protein interfaces reveals targets for synthetic inhibitors
- PMID: 20712375
- PMCID: PMC2955827
- DOI: 10.1021/cb1001747
Systematic analysis of helical protein interfaces reveals targets for synthetic inhibitors
Abstract
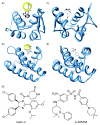
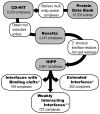
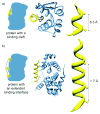
Synthetic inhibitors of protein-protein interactions are being discovered despite the inherent challenge in targeting large contact surfaces with small molecules. An analysis of available examples identifies common features of complexes that make them tractable for small molecules. We deduced that relative disposition and energetic contributions of "hot spot" residues provide a predictive scale for the potential of protein-protein interactions to be inhibited by small molecules. On the basis of this model, we analyzed the full set of helical protein interfaces in the Protein Data Bank to identify those that are potentially suitable candidates for synthetic ligands.
Figures
References
-
- Wells JA, McClendon CL. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature. 2007;450:1001–1009. - PubMed
-
- Bogan AA, Thorn KS. Anatomy of hot spots in protein interfaces. J Mol Biol. 1998;280:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Moreira IS, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ. Hot spots--a review of the protein-protein interface determinant amino-acid residues. Proteins. 2007;68:803–812. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham BC, Wells JA. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989;244:1081–1085. - PubMed
-
- Kussie PH, Gorina S, Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Moreau J, Levine AJ, Pavletich NP. Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain. Science. 1996;274:948–953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

