NOX3 NADPH oxidase couples transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 to signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-mediated inflammation and hearing loss
- PMID: 20712533
- PMCID: PMC3043978
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3497
NOX3 NADPH oxidase couples transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 to signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-mediated inflammation and hearing loss
Abstract
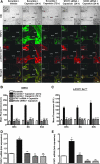
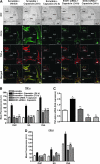
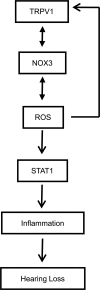
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) is implicated in cisplatin ototoxicity. Activation of this channel by cisplatin increases reactive oxygen species generation, which contribute to loss of outer hair cells in the cochlea. Knockdown of TRPV1 by short interfering RNA protected against cisplatin ototoxicity. In this study, we examined the mechanism underlying TRPV1-mediated ototoxicity using cultured organ of Corti transformed cells (UB/OC-1) and rats. Trans-tympanic injections of capsaicin produced transient hearing loss within 24 h, which recovered by 72 h. In UB/OC-1 cells, capsaicin increased NOX3 NADPH oxidase activity and activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1). Intratympanic administration of capsaicin transiently increased STAT1 activity and expression of downstream proinflammatory molecules. Capsaicin produced a transient increase in CD14-positive inflammatory cells into the cochlea, which mimicked the temporal course of STAT1 activation but did not alter the expression of apoptotic genes or damage to outer hair cells. In addition, trans-tympanic administration of STAT1 short interfering RNA protected against capsaicin-induced hearing loss. These data suggest that activation of TRPV1 mediates temporary hearing loss by initiating an inflammatory process in the cochlea via activation of NOX3 and STAT1. Thus, these proteins represent reasonable targets for ameliorating hearing loss.
Figures
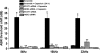
Similar articles
-
Adenosine A1 Receptor Protects Against Cisplatin Ototoxicity by Suppressing the NOX3/STAT1 Inflammatory Pathway in the Cochlea.J Neurosci. 2016 Apr 6;36(14):3962-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3111-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27053204 Free PMC article.
-
Short interfering RNA against STAT1 attenuates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in the rat by suppressing inflammation.Cell Death Dis. 2011 Jul 21;2(7):e180. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.63. Cell Death Dis. 2011. PMID: 21776018 Free PMC article.
-
Short interfering RNA against transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;28(49):13056-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1307-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19052196 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Auditory Functions.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Jun;36(16-18):1158-1170. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0191. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34465184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
siRNA-mediated knock-down of NOX3: therapy for hearing loss?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(14):2429-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1016-3. Epub 2012 May 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22562580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Redox Implications of Extreme Task Performance: The Case in Driver Athletes.Cells. 2022 Mar 5;11(5):899. doi: 10.3390/cells11050899. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calpain mediated cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in mice.Neural Regen Res. 2013 Jul 25;8(21):1995-2002. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.21.008. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206508 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing loss during chemotherapy: prevalence, mechanisms, and protection.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 25;14(9):4597-4632. doi: 10.62347/OKGQ4382. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aminoglycoside- and Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Mechanisms and Otoprotective Strategies.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Nov 1;9(11):a033548. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033548. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 30559254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of myricetin on the gene expressions of NOX3, TGF-β1, prestin, and HSP-70 and anti-oxidant activity in the cochlea of noise-exposed rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 May;23(5):594-599. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2020.41007.9693. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32742596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alawi K. Keeble J. The paradoxical role of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 receptor in inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 2010;125:181–195. - PubMed
-
- Bánfi B. Malgrange B. Knisz J. Steger K. Dubois-Dauphin M. Krause K-H. NOX3, a superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of the inner ear. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:46065–46072. - PubMed
-
- Birder LA. Nakamura Y. Kiss S. Nealen ML. Barrick S. Kanai AJ. Wang E. Ruiz G. De Groat WC. Apodaca G. Watkins S. Caterina MJ. Altered urinary bladder function in mice lacking the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:856–860. - PubMed
-
- Christoph T. Grünweller A. Mika J. Schäfer MK. Wade EJ. Weihe E. Erdmann VA. Frank R. Gillen C. Kurreck J. Silencing of vanilloid receptor TRPV1 by RNAi reduces neuropathic and visceral pain in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;350:238–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

