Cadmium suppresses the proliferation of piglet Sertoli cells and causes their DNA damage, cell apoptosis and aberrant ultrastructure
- PMID: 20712887
- PMCID: PMC3224921
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-97
Cadmium suppresses the proliferation of piglet Sertoli cells and causes their DNA damage, cell apoptosis and aberrant ultrastructure
Abstract
Objective: Very little information is known about the toxic effects of cadmium on somatic cells in mammalian testis. The objective of this study is to explore the toxicity of cadmium on piglet Sertoli cells.
Methods: Sertoli cells were isolated from piglet testes using a two-step enzyme digestion and followed by differential plating. Piglet Sertoli cells were identified by oil red O staining and Fas ligand (FasL) expression as assayed by immunocytochemistry and expression of transferrin and androgen binding protein by RT-PCR. Sertoli cells were cultured in DMEM/F12 supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum in the absence or presence of various concentrations of cadmium chloride, or treatment with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190 and with cadmium chloride exposure. Apoptotic cells in seminiferous tubules of piglets were also performed using TUNEL assay in vivo.
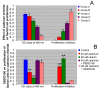
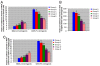
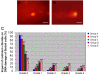
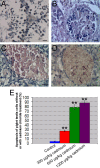
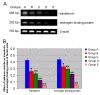
Results: Cadmium chloride inhibited the proliferation of Piglet Sertoli cells as shown by MTT assay, and it increased malondialdehyde (MDA) but reduced superoxide dismutase (SOD) and Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity. Inhibitor SB202190 alleviated the proliferation inhibition of cadmium on piglet Sertoli cells. Comet assay revealed that cadmium chloride caused DNA damage of Piglet Sertoli cells and resulted in cell apoptosis as assayed by flow cytometry. The in vivo study confirmed that cadmium induced cell apoptosis in seminiferous tubules of piglets. Transmission electronic microscopy showed abnormal and apoptotic ultrastructure in Piglet Sertoli cells treated with cadmium chloride compared to the control.
Conclusion: cadmium has obvious adverse effects on the proliferation of piglet Sertoli cells and causes their DNA damage, cell apoptosis, and aberrant morphology. This study thus offers novel insights into the toxicology of cadmium on male reproduction.
Figures


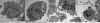
Similar articles
-
DNA damage and decrease of cellular oxidase activity in piglet Sertoli cells exposed to arsanilic acid.J Vet Med Sci. 2011 Feb;73(2):199-203. doi: 10.1292/jvms.10-0236. Epub 2010 Oct 7. J Vet Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 20944440
-
Protective Mechanism of Sulforaphane on Cadmium-Induced Sertoli Cell Injury in Mice Testis via Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2018 Jul 19;23(7):1774. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071774. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30029485 Free PMC article.
-
Lycopene attenuates zearalenone-induced oxidative damage of piglet sertoli cells through the nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 signaling pathway.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Dec 1;225:112737. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112737. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 34482067
-
Sensitivity of Sertoli and Leydig cells to xenobiotics in in vitro models.Reprod Toxicol. 1993;7 Suppl 1:23-37. doi: 10.1016/0890-6238(93)90066-g. Reprod Toxicol. 1993. PMID: 8400637 Review.
-
Toxic Effect of Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic on the Sertoli Cell: Mechanisms of Damage Involved.DNA Cell Biol. 2018 Jul;37(7):600-608. doi: 10.1089/dna.2017.4081. Epub 2018 May 10. DNA Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29746152 Review.
Cited by
-
Impacts of environmental toxicants on male reproductive dysfunction.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011 May;32(5):290-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21324536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sperm motility and morphology changes in rats exposed to cadmium and diazinon.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016 Aug 8;14(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12958-016-0177-6. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27503218 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc and low-dose of cadmium protect sertoli cells against toxic-dose of cadmium: The role of metallothionein.Iran J Reprod Med. 2013 Jun;11(6):487-94. Iran J Reprod Med. 2013. PMID: 24639783 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium and proliferation in human uterine leiomyoma cells: evidence of a role for EGFR/MAPK pathways but not classical estrogen receptor pathways.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Apr;123(4):331-6. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408234. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 25343777 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc restores functionality in porcine prepubertal Sertoli cells exposed to subtoxic cadmium concentration via regulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 10;14:962519. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.962519. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36843583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nicholson JK, Higham DP, Timbrell JA, Sadler PJ. Quantitative high resolution 1H NMR urinalysis studies on the biochemical effects of cadmium in the rat. Mol Pharmacol. 1989;36:398–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

