Regulatory T cell frequency in patients with melanoma with different disease stage and course, and modulating effects of high-dose interferon-alpha 2b treatment
- PMID: 20712892
- PMCID: PMC2936304
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-76
Regulatory T cell frequency in patients with melanoma with different disease stage and course, and modulating effects of high-dose interferon-alpha 2b treatment
Abstract
Background: High-dose interferon-alpha 2b (IFN-alpha 2b) is the only approved systemic therapy in the United States for the adjuvant treatment of melanoma. The study objective was to explore the immunomodulatory mechanism of action for IFN-alpha 2b by measuring serum regulatory T cell (Treg), serum transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), interleukin (IL)-10, and autoantibody levels in patients with melanoma treated with the induction phase of the high-dose IFN-alpha 2b regimen.
Methods: Patients with melanoma received IFN-alpha 2b administered intravenously (20 MU/m2 each day from day 1 to day 5 for 4 consecutive weeks). Serum Treg levels were measured as whole lymphocytes in CD4+ cells using flow cytometry while TGF-beta, IL-10, and autoantibody levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
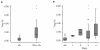
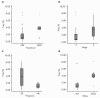
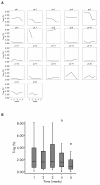
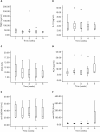
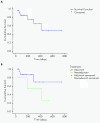
Results: Twenty-two patients with melanoma received IFN-alpha 2b treatment and were evaluated for Treg levels. Before treatment, Treg levels were significantly higher in patients with melanoma when compared with data from 20 healthy subjects (P = 0.001; Mann-Whitney test). Although a trend for reduction of Treg levels following IFN-α 2b treatment was observed (average decrease 0.29% per week), statistical significance was not achieved. Subgroup analyses indicated higher baseline Treg levels for stage III versus IV disease (P = 0.082), early recurrence versus no recurrence (P = 0.017), deceased versus surviving patients (P = 0.021), and preoperative neoadjuvant versus postoperative adjuvant treatment groups (not significant). No significant effects were observed on the levels of TGF-beta, IL-10, and autoantibodies in patients with melanoma treated with IFN-alpha 2b.
Conclusions: Patients with melanoma in this study showed increased basal levels of Treg that may be relevant to their disease and its progression. Treg levels shifted in patients with melanoma treated with IFN-alpha 2b, although no firm conclusions regarding the role of Tregs as a marker of treatment response or outcome can be made at present.
Figures

References
-
- Fecher LA, Flaherty KT. Where are we with adjuvant therapy of stage III and IV melanoma in 2009? J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2009;7:295–304. - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sondak VK, Richards J, Flaherty LE, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Rao U, Steele M, Blum RH. High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2444–2458. - PubMed
-
- Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Santinami M, Testori A, Kruit WH, Marsden J, Punt CJ, Salès F, Gore M, Mackie R, Kusic Z, Dummer R, Hauschild A, Musat E, Spatz A, Keilholz U. Adjuvant therapy with pegylated interferon alfa-2b versus observation alone in resected stage III melanoma: final results of EORTC 18991 a randomised phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:117–126. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61033-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

