Mitochondrial free [Ca2+] increases during ATP/ADP antiport and ADP phosphorylation: exploration of mechanisms
- PMID: 20712982
- PMCID: PMC2920628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.04.069
Mitochondrial free [Ca2+] increases during ATP/ADP antiport and ADP phosphorylation: exploration of mechanisms
Erratum in
- Biophys J. 2010 Dec 15;99(12):4078
Abstract
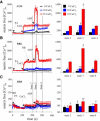
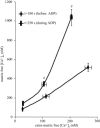
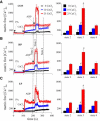
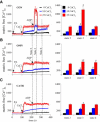
ADP influx and ADP phosphorylation may alter mitochondrial free [Ca2+] ([Ca2+](m)) and consequently mitochondrial bioenergetics by several postulated mechanisms. We tested how [Ca2+](m) is affected by H2PO4(-) (P(i)), Mg2+, calcium uniporter activity, matrix volume changes, and the bioenergetic state. We measured [Ca2+](m), membrane potential, redox state, matrix volume, pH(m), and O2 consumption in guinea pig heart mitochondria with or without ruthenium red, carboxyatractyloside, or oligomycin, and at several levels of Mg2+ and P(i). Energized mitochondria showed a dose-dependent increase in [Ca2+](m) after adding CaCl2 equivalent to 20, 114, and 485 nM extramatrix free [Ca2+] ([Ca2+](e)); this uptake was attenuated at higher buffer Mg2+. Adding ADP transiently increased [Ca2+](m) up to twofold. The ADP effect on increasing [Ca2+](m) could be partially attributed to matrix contraction, but was little affected by ruthenium red or changes in Mg2+ or P(i). Oligomycin largely reduced the increase in [Ca2+](m) by ADP compared to control, and [Ca2+](m) did not return to baseline. Carboxyatractyloside prevented the ADP-induced [Ca2+](m) increase. Adding CaCl2 had no effect on bioenergetics, except for a small increase in state 2 and state 4 respiration at 485 nM [Ca2+](e). These data suggest that matrix ADP influx and subsequent phosphorylation increase [Ca2+](m) largely due to the interaction of matrix Ca2+ with ATP, ADP, P(i), and cation buffering proteins in the matrix.
2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Brandes R., Bers D.M. Intracellular Ca2+ increases the mitochondrial NADH concentration during elevated work in intact cardiac muscle. Circ. Res. 1997;80:82–87. - PubMed
-
- McCormack J.G., Halestrap A.P., Denton R.M. Role of calcium ions in regulation of mammalian intramitochondrial metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 1990;70:391–425. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen M.H., Dudycha S.J., Jafri M.S. Effect of Ca2+ on cardiac mitochondrial energy production is modulated by Na+ and H+ dynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C2004–C2020. - PubMed
-
- Rossi C.S., Lehninger A.L. Stoichiometry of respiratory stimulation, accumulation of Ca++ and phosphate, and oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1964;239:3971–3980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

