Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of membrane-associated myelin basic protein--conformation and dynamics of an immunodominant epitope
- PMID: 20713009
- PMCID: PMC2920716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.022
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of membrane-associated myelin basic protein--conformation and dynamics of an immunodominant epitope
Abstract
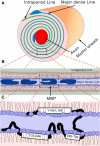
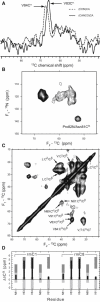
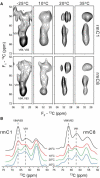
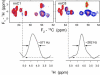
Myelin basic protein (MBP) maintains the tight multilamellar compaction of the myelin sheath in the central nervous system through peripheral binding of adjacent lipid bilayers of oligodendrocytes. Myelin instability in multiple sclerosis (MS) is associated with the loss of positive charge in MBP as a result of posttranslational enzymatic deimination. A highly-conserved central membrane-binding fragment (murine N81-PVVHFFKNIVTPRTPPP-S99, identical to human N83-S101) represents a primary immunodominant epitope in MS. Previous low-resolution electron paramagnetic resonance measurements on the V83-T92 fragment, with Cys-mutations and spin-labeling that scanned the epitope, were consistent with it being a membrane-associated amphipathic alpha-helix. Pseudodeimination at several sites throughout the protein, all distal to the central segment, disrupted the alpha-helix at its amino-terminus and exposed it to proteases, representing a potential mechanism in the autoimmune pathogenesis of MS. Here, we have used magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy to characterize more precisely the molecular conformation and dynamics of this central immunodominant epitope of MBP in a lipid milieu, without Cys-substitution. Our solid-state NMR measurements have revealed that the alpha-helix present within the immunodominant epitope is shorter than originally modeled, and is independent of the pseudodeimination, highlighting the importance of the local hydrophobic effects in helix formation and stability. The main effect of pseudodeimination is to cause the cytoplasmic exposure of the fragment, potentially making it more accessible to proteolysis. These results are the first, to our knowledge, to provide atomic-level detail of a membrane-anchoring segment of MBP, and direct evidence of decreased MBP-membrane interaction after posttranslational modification.
2010 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
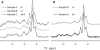
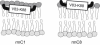
Similar articles
-
Deimination of membrane-bound myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis exposes an immunodominant epitope.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 21;103(12):4422-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509158103. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16537438 Free PMC article.
-
Adduction of cholesterol 5,6-secosterol aldehyde to membrane-bound myelin basic protein exposes an immunodominant epitope.Biochemistry. 2011 Mar 29;50(12):2092-100. doi: 10.1021/bi200109q. Epub 2011 Feb 28. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21314187 Free PMC article.
-
Solution NMR structure of an immunodominant epitope of myelin basic protein. Conformational dependence on environment of an intrinsically unstructured protein.FEBS J. 2006 Feb;273(3):601-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.05093.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16420483
-
The classic basic protein of myelin--conserved structural motifs and the dynamic molecular barcode involved in membrane adhesion and protein-protein interactions.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009 Jun;10(3):196-215. doi: 10.2174/138920309788452218. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19519451 Review.
-
MyelStones: the executive roles of myelin basic protein in myelin assembly and destabilization in multiple sclerosis.Biochem J. 2015 Nov 15;472(1):17-32. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150710. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26518750 Review.
Cited by
-
Oligodendroglial membrane dynamics in relation to myelin biogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Sep;73(17):3291-310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2228-8. Epub 2016 May 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27141942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atomic resolution view into the structure-function relationships of the human myelin peripheral membrane protein P2.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Jan;70(Pt 1):165-76. doi: 10.1107/S1399004713027910. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 24419389 Free PMC article.
-
The magic of bicelles lights up membrane protein structure.Chem Rev. 2012 Nov 14;112(11):6054-74. doi: 10.1021/cr300061w. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Chem Rev. 2012. PMID: 22920148 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Surface-Binding to Cardiolipin Nanodomains Triggers Cytochrome c Pro-apoptotic Peroxidase Activity via Localized Dynamics.Structure. 2019 May 7;27(5):806-815.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.02.007. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Structure. 2019. PMID: 30879887 Free PMC article.
-
Myelin Basic Protein Citrullination in Multiple Sclerosis: A Potential Therapeutic Target for the Pathology.Neurochem Res. 2016 Aug;41(8):1845-56. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1920-2. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27097548 Review.
References
-
- Boggs J.M., Bates I.R., Harauz G. Interactions of the 18.5 kDa myelin basic protein (MBP) with lipid bilayers—studies by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy and implications for generation of autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis. In: Boggs J.M., editor. Myelin Basic Protein. Nova Science; New York: 2008.
-
- Boggs J.M. Myelin basic protein interactions with actin and tubulin in vitro—binding, assembly, and regulation. In: Boggs J.M., editor. Myelin Basic Protein. Nova Science; New York: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

