Specific inhibition of a pathogenic receptor tyrosine kinase by its transmembrane domain
- PMID: 20713021
- PMCID: PMC2994959
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.08.007
Specific inhibition of a pathogenic receptor tyrosine kinase by its transmembrane domain
Abstract
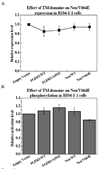
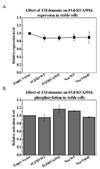
The transmembrane (TM) domains of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are believed to be important players in RTK signal transduction. However, the degree of specificity and promiscuity of RTK TM domain lateral interactions in mammalian membranes has not been assessed in detail in the literature. A technique to probe the occurrence of interactions between TM domains and their biological significance is to evaluate the propensity for formation of heterodimers of a full-length RTK and its TM domain. Here we examine if the inhibition of two RTK pathogenic mutants, Neu/V664E and FGFR3/A391E, can be achieved by the TM domains of Neu, Neu/V664E, FGFR3 and FGFR3/A391E. We show that the TM domain of Neu/V664E specifically inhibits the phosphorylation of full-length Neu/V664E, while the wild-type Neu TM domain does not. In addition, Neu/V664E TM domain does not affect the phosphorylation levels of full-length FGFR3/A391E. The results suggest that TM domain peptides could be exploited in the future for the development of specific inhibitors of mutant RTKs.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
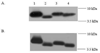
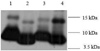
Similar articles
-
Pathogenic activation of receptor tyrosine kinases in mammalian membranes.J Mol Biol. 2008 Dec 31;384(5):1130-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.036. Epub 2008 Oct 19. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18976668
-
High-throughput selection of transmembrane sequences that enhance receptor tyrosine kinase activation.J Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 9;412(1):43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.07.004. Epub 2011 Jul 12. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21767549 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of receptor tyrosine kinase transmembrane domain interactions: the EmEx-FRET method.J Membr Biol. 2007 Feb;215(2-3):93-103. doi: 10.1007/s00232-007-9009-0. Epub 2007 Jun 14. J Membr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17565424 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase transmembrane domains: Function, dimer structure and dimerization energetics.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Apr-Jun;4(2):249-54. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.2.10725. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20168077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of receptor tyrosine kinase transmembrane domains in cell signaling and human pathologies.Biochemistry. 2006 May 23;45(20):6241-51. doi: 10.1021/bi060609y. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16700535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strong dimerization of wild-type ErbB2/Neu transmembrane domain and the oncogenic Val664Glu mutant in mammalian plasma membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1838(9):2326-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24631664 Free PMC article.
-
The HIV-1 envelope transmembrane domain binds TLR2 through a distinct dimerization motif and inhibits TLR2-mediated responses.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Aug 14;10(8):e1004248. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004248. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25121610 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane helix dimerization: beyond the search for sequence motifs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1818(2):183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.08.031. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21910966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane receptor activation mechanisms and transmembrane peptide tools to elucidate them.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 14;295(7):1792-1814. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.009457. Epub 2019 Dec 25. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31879273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo-designed transmembrane proteins bind and regulate a cytokine receptor.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Jun;20(6):751-760. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01562-z. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38480980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schlessinger J. Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell. 2002;110:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Eswarakumar VP, Lax I, Schlessinger J. Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Common and distinct elements in cellular signaling via EGF and FGF receptors. Science. 2004;306:1506–1507. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Gureasko J, Shen K, Cole PA, Kuriyan J. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell. 2006;125:1137–1149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

