DNA minor groove induced dimerization of heterocyclic cations: compound structure, binding affinity, and specificity for a TTAA site
- PMID: 20713062
- PMCID: PMC2988403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.018
DNA minor groove induced dimerization of heterocyclic cations: compound structure, binding affinity, and specificity for a TTAA site
Abstract
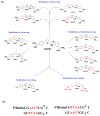
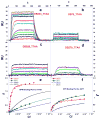
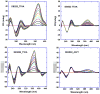
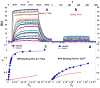
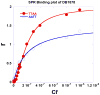
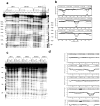
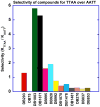
With the increasing number and variations of genome sequences available, control of gene expression with synthetic, cell-permeable molecules is within reach. The variety of sequence-specific binding agents is, however, still quite limited. Many minor groove binding agents selectivity recognize AT over GC sequences but have less ability to distinguish among different AT sequences. The goal with this article is to develop compounds that can bind selectively to different AT sequences. A number of studies indicate that AATT and TTAA sequences have significantly different physical and interaction properties and different requirements for minor groove recognition. Although it has been difficult to get minor groove binding at TTAA, DB293, a phenyl-furan-benzimidazole diamidine, was found to bind as a strong, cooperative dimer at TTAA but with no selectivity over AATT. In order to improve selectivity, we made modifications to each unit of DB293. Binding affinities and stoichiometries obtained from biosensor-surface plasmon resonance experiments show that DB1003, a furan-furan-benzimidazole diamidine, binds strongly to TTAA as a dimer and has selectivity (K(TTAA)/K(AATT)=6). CD and DNase I footprinting studies confirmed the preference of this compound for TTAA. In summary, (i) a favorable stacking surface provided by the pi system, (ii) H-bond donors to interact with TA base pairs at the floor of the groove provided by a benzimidazole (or indole) -NH and amidines, and (iii) appropriate curvature of the dimer complex to match the curvature of the minor groove play important roles in differentiating the TTAA and AATT minor grooves.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Dervan PB. Design of sequence-specific DNA-binding molecules. Science. 1986;232:464–71. - PubMed
-
- Soeiro MN, de Castro SL. Trypanosoma cruzi targets for new chemotherapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009;13:105–21. - PubMed
-
- Motta MC. Kinetoplast as a potential chemotherapeutic target of trypanosomatids. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14:847–54. - PubMed
-
- Hebert MD. Targeting the gene in Friedreich ataxia. Biochimie. 2008;90:1131–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

