Regulation of nucleolar chromatin by B23/nucleophosmin jointly depends upon its RNA binding activity and transcription factor UBF
- PMID: 20713446
- PMCID: PMC2950543
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00299-10
Regulation of nucleolar chromatin by B23/nucleophosmin jointly depends upon its RNA binding activity and transcription factor UBF
Abstract
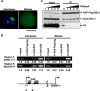
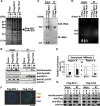
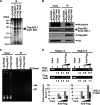
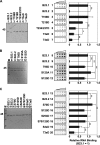
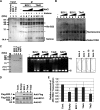
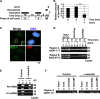
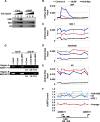
Histone chaperones regulate the density of incorporated histone proteins around DNA transcription sites and therefore constitute an important site-specific regulatory mechanism for the control of gene expression. At present, the targeting mechanism conferring this site specificity is unknown. We previously reported that the histone chaperone B23/nucleophosmin associates with rRNA chromatin (r-chromatin) to stimulate rRNA transcription. Here, we report on the mechanism for site-specific targeting of B23 to the r-chromatin. We observed that, during mitosis, B23 was released from chromatin upon inactivation of its RNA binding activity by cdc2 kinase-mediated phosphorylation. The phosphorylation status of B23 was also shown to strongly affect its chromatin binding activity. We further found that r-chromatin binding of B23 was a necessary condition for B23 histone chaperone activity in vivo. In addition, we found that depletion of upstream binding factor (UBF; an rRNA transcription factor) decreased the chromatin binding affinity of B23, which in turn led to an increase in histone density at the r-chromatin. These two major strands of evidence suggest a novel cell cycle-dependent mechanism for the site-specific regulation of histone density via joint RNA- and transcription factor-mediated recruitment of histone chaperones to specific chromosome loci.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription regulation of the rRNA gene by a multifunctional nucleolar protein, B23/nucleophosmin, through its histone chaperone activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(10):3114-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02078-07. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18332108 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar localization of aprataxin is dependent on interaction with nucleolin and on active ribosomal DNA transcription.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Jul 15;15(14):2239-49. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl149. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16777843
-
Identification of nucleophosmin/B23, an acidic nucleolar protein, as a stimulatory factor for in vitro replication of adenovirus DNA complexed with viral basic core proteins.J Mol Biol. 2001 Aug 3;311(1):41-55. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4812. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11469856
-
Chromatin: linking structure and function in the nucleolus.Chromosoma. 2009 Feb;118(1):11-23. doi: 10.1007/s00412-008-0184-2. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Chromosoma. 2009. PMID: 18925405 Review.
-
A role for upstream binding factor in organizing ribosomal gene chromatin.Biochem Soc Symp. 2006;(73):77-84. doi: 10.1042/bss0730077. Biochem Soc Symp. 2006. PMID: 16626289 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 in Translational Regulation in the M-Phase.Cells. 2020 Jun 27;9(7):1568. doi: 10.3390/cells9071568. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32605021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleophosmin deposition during mRNA 3' end processing influences poly(A) tail length.EMBO J. 2011 Aug 5;30(19):3994-4005. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.272. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21822216 Free PMC article.
-
Alu element-containing RNAs maintain nucleolar structure and function.EMBO J. 2015 Nov 12;34(22):2758-74. doi: 10.15252/embj.201591458. Epub 2015 Oct 13. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 26464461 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteome Profiling Reveals Multifunctional Protein NPM1 as part of the Irradiation Response of Tumor Cells.Transl Oncol. 2019 Feb;12(2):308-319. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30453269 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient DNA binding of NF-κB requires the chaperone-like function of NPM1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Apr 20;45(7):3707-3723. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1285. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28003476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conconi, A., R. M. Widmer, T. Koller, and J. M. Sogo. 1989. Two different chromatin structures coexist in ribosomal RNA genes throughout the cell cycle. Cell 57:753-761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
