Prenatal androgen exposure programs metabolic dysfunction in female mice
- PMID: 20713501
- PMCID: PMC3612271
- DOI: 10.1677/JOE-10-0217
Prenatal androgen exposure programs metabolic dysfunction in female mice
Abstract
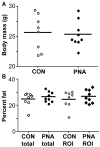
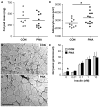
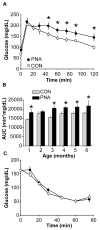
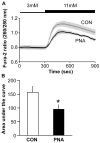
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common fertility disorder with metabolic sequelae. Our laboratory previously characterized reproductive phenotypes in a prenatally androgenized (PNA) mouse model for PCOS. PNA mice exhibited elevated testosterone and LH levels, irregular estrous cycles, and neuroendocrine abnormalities suggesting increased central drive to the reproductive system. In this study, we examined metabolic characteristics of female PNA mice. PNA mice exhibited increased fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) that were independent of age and were not associated with changes in body composition or peripheral insulin sensitivity. IGT was associated with defects in pancreatic islet function leading to an impaired response to high glucose, consistent with impaired insulin secretion. Exposure of isolated pancreatic islets to androgen in vitro demonstrated an impaired response to glucose stimulation similar to that in PNA mice, suggesting androgens may have activational in addition to organizational effects on pancreatic islet function. PNA mice also exhibited increased size of visceral adipocytes, suggesting androgen-programed differences in adipocyte differentiation and/or function. These studies demonstrate that in addition to causing reproductive axis abnormalities, in utero androgen exposure can induce long-term metabolic alterations in female mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Abbott DH, Barnett DK, Bruns CM, Dumesic DA. Androgen excess fetal programming of female reproduction: a developmental aetiology for polycystic ovary syndrome? Hum Reprod Update. 2005;11:357–374. - PubMed
-
- Amiel SA, Sherwin RS, Simonson DC, Lauritano AA, Tamborlane WV. Impaired insulin action in puberty. A contributing factor to poor glycemic control in adolescents with diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1986;315:215–219. - PubMed
-
- Arnold AP, Breedlove SM. Organizational and activational effects of sex steroids on brain and behavior: a reanalysis. Horm Behav. 1985;19:469–498. - PubMed
-
- Blouin K, Veilleux A, Luu-The V, Tchernof A. Androgen metabolism in adipose tissue: recent advances. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;301:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Bock G, Chittilapilly E, Basu R, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Chandramouli V, Landau BR, Rizza R. Contribution of hepatic and extrahepatic insulin resistance to the pathogenesis of impaired fasting glucose: role of increased rates of gluconeogenesis. Diabetes. 2007;56:1703–1711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

