Systematic screen reveals new functional dynamics of histones H3 and H4 during gametogenesis
- PMID: 20713519
- PMCID: PMC2922505
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1954910
Systematic screen reveals new functional dynamics of histones H3 and H4 during gametogenesis
Abstract
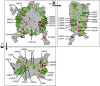
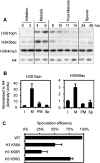
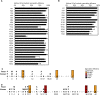
Profound epigenetic differences exist between genomes derived from male and female gametes; however, the nature of these changes remains largely unknown. We undertook a systematic investigation of chromatin reorganization during gametogenesis, using the model eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae to examine sporulation, which has strong similarities with higher eukaryotic spermatogenesis. We established a mutational screen of histones H3 and H4 to uncover substitutions that reduce sporulation efficiency. We discovered two patches of residues-one on H3 and a second on H4-that are crucial for sporulation but not critical for mitotic growth, and likely comprise interactive nucleosomal surfaces. Furthermore, we identified novel histone post-translational modifications that mark the chromatin reorganization process during sporulation. First, phosphorylation of H3T11 appears to be a key modification during meiosis, and requires the meiotic-specific kinase Mek1. Second, H4 undergoes amino tail acetylation at Lys 5, Lys 8, and Lys 12, and these are synergistically important for post-meiotic chromatin compaction, occurring subsequent to the post-meiotic transient peak in phosphorylation at H4S1, and crucial for recruitment of Bdf1, a bromodomain protein, to chromatin in mature spores. Strikingly, the presence and temporal succession of the new H3 and H4 modifications are detected during mouse spermatogenesis, indicating that they are conserved through evolution. Thus, our results show that investigation of gametogenesis in yeast provides novel insights into chromatin dynamics, which are potentially relevant to epigenetic modulation of the mammalian process.
Figures
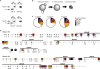


Similar articles
-
Systematic genetic and proteomic screens during gametogenesis identify H2BK34 methylation as an evolutionary conserved meiotic mark.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2020 Sep 15;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13072-020-00349-5. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2020. PMID: 32933557 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of histone H4 Ser1 regulates sporulation in yeast and is conserved in fly and mouse spermatogenesis.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 15;20(18):2580-92. doi: 10.1101/gad.1457006. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16980586 Free PMC article.
-
Splitting of H3-H4 tetramers at transcriptionally active genes undergoing dynamic histone exchange.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1296-301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018308108. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21220302 Free PMC article.
-
Packing for the germy: the role of histone H4 Ser1 phosphorylation in chromatin compaction and germ cell development.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 15;20(18):2487-91. doi: 10.1101/gad.1477706. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16980578 Review. No abstract available.
-
Spanning the gap: unraveling RSC dynamics in vivo.Curr Genet. 2021 Jun;67(3):399-406. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01144-1. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33484328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The linker histone plays a dual role during gametogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jul;32(14):2771-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00282-12. Epub 2012 May 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22586276 Free PMC article.
-
Point mutations in an epigenetic factor lead to multiple types of bone tumors: role of H3.3 histone variant in bone development and disease.Bonekey Rep. 2015 Jul 1;4:715. doi: 10.1038/bonekey.2015.84. eCollection 2015. Bonekey Rep. 2015. PMID: 26157578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H3 threonine 11 phosphorylation by Sch9 and CK2 regulates chronological lifespan by controlling the nutritional stress response.Elife. 2018 Jun 25;7:e36157. doi: 10.7554/eLife.36157. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29938647 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct requirements for the COMPASS core subunits Set1, Swd1, and Swd3 during meiosis in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Oct 19;11(11):jkab283. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab283. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 34849786 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic analysis of gametogenesis reveals a novel signature at the promoters and distal enhancers of active genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 May 7;48(8):4115-4138. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa163. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32182340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barber CM, Turner FB, Wang Y, Hagstrom K, Taverna SD, Mollah S, Ueberheide B, Meyer BJ, Hunt DF, Cheung P, et al. 2004. The enhancement of histone H4 and H2A serine 1 phosphorylation during mitosis and S-phase is evolutionarily conserved. Chromosoma 112: 360–371 - PubMed
-
- Berger SL 2007. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447: 407–412 - PubMed
-
- Chikashige Y, Hiraoka Y 2001. Telomere binding of the Rap1 protein is required for meiosis in fission yeast. Curr Biol 11:1618–1623 - PubMed
-
- Cho C, Willis WD, Goulding EH, Jung-Ha H, Choi YC, Hecht NB, Eddy EM 2001. Haploinsufficiency of protamine-1 or -2 causes infertility in mice. Nat Genet 28: 82–86 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
