A novel interaction between FlnA and Syk regulates platelet ITAM-mediated receptor signaling and function
- PMID: 20713593
- PMCID: PMC2931168
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100222
A novel interaction between FlnA and Syk regulates platelet ITAM-mediated receptor signaling and function
Abstract
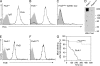
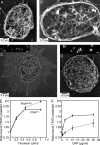
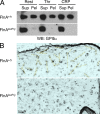
Filamin A (FlnA) cross-links actin filaments and connects the Von Willebrand factor receptor GPIb-IX-V to the underlying cytoskeleton in platelets. Because FlnA deficiency is embryonic lethal, mice lacking FlnA in platelets were generated by breeding FlnA(loxP/loxP) females with GATA1-Cre males. FlnA(loxP/y) GATA1-Cre males have a macrothrombocytopenia and increased tail bleeding times. FlnA-null platelets have decreased expression and altered surface distribution of GPIbalpha because they lack the normal cytoskeletal linkage of GPIbalpha to underlying actin filaments. This results in approximately 70% less platelet coverage on collagen-coated surfaces at shear rates of 1,500/s, compared with wild-type platelets. Unexpectedly, however, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)- and ITAM-like-mediated signals are severely compromised in FlnA-null platelets. FlnA-null platelets fail to spread and have decreased alpha-granule secretion, integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation, and protein tyrosine phosphorylation, particularly that of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk and phospholipase C-gamma2, in response to stimulation through the collagen receptor GPVI and the C-type lectin-like receptor 2. This signaling defect was traced to the loss of a novel FlnA-Syk interaction, as Syk binds to FlnA at immunoglobulin-like repeat 5. Our findings reveal that the interaction between FlnA and Syk regulates ITAM- and ITAM-like-containing receptor signaling and platelet function.
Figures
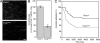


References
-
- Asazuma N., Ozaki Y., Satoh K., Yatomi Y., Handa M., Fujimura Y., Miura S., Kume S. 1997. Glycoprotein Ib-von Willebrand factor interactions activate tyrosine kinases in human platelets. Blood. 90:4789–4798 - PubMed
-
- Boylan B., Berndt M.C., Kahn M.L., Newman P.J. 2006. Activation-independent, antibody-mediated removal of GPVI from circulating human platelets: development of a novel NOD/SCID mouse model to evaluate the in vivo effectiveness of anti-human platelet agents. Blood. 108:908–914 10.1182/blood-2005-07-2937 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clark E.A., Shattil S.J., Ginsberg M.H., Bolen J., Brugge J.S. 1994. Regulation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp72syk by platelet agonists and the integrin α IIb beta 3. J. Biol. Chem. 269:28859–28864 - PubMed
-
- Cranmer S.L., Ulsemer P., Cooke B.M., Salem H.H., de la Salle C., Lanza F., Jackson S.P. 1999. Glycoprotein (GP) Ib-IX-transfected cells roll on a von Willebrand factor matrix under flow. Importance of the GPib/actin-binding protein (ABP-280) interaction in maintaining adhesion under high shear. J. Biol. Chem. 274:6097–6106 10.1074/jbc.274.10.6097 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

