LT-IIc, a new member of the type II heat-labile enterotoxin family encoded by an Escherichia coli strain obtained from a nonmammalian host
- PMID: 20713622
- PMCID: PMC2976314
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00730-10
LT-IIc, a new member of the type II heat-labile enterotoxin family encoded by an Escherichia coli strain obtained from a nonmammalian host
Abstract
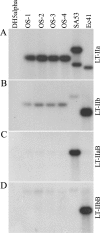
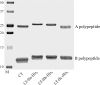
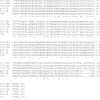
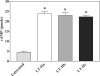
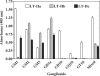
Two families of bacterial heat-labile enterotoxins (HLTs) have been described: the type I HLTs are comprised of cholera toxin (CT) of Vibrio cholerae, LT-I of Escherichia coli, and several related HLTs; the type II HLTs are comprised of LT-IIa and LT-IIb. Herein, we report LT-IIc, a new type II HLT encoded from an enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) strain isolated from an avian host. Using a mouse Y1 adrenal cell bioassay, LT-IIc was shown to be less cytotoxic than CT, LT-IIa, or LT-IIb. Cytotoxicity of LT-IIc was partially neutralized by antisera recognizing LT-IIa or LT-IIb but not by anti-CT antiserum. Genes encoding putative A polypeptide and B polypeptides of LT-IIc were arranged in an operon which was flanked by potential prophage sequences. Analysis of the nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences demonstrated that the A polypeptide of LT-IIc has moderate homology to the A polypeptides of CT and LT-I and high homology to the A polypeptides of LT-IIa and LT-IIb. The B polypeptide of LT-IIc exhibited no significant homology to the B polypeptides of CT and LT-I and only moderate homology to the B polypeptides of LT-IIa and LT-IIb. The binding pattern of LT-IIc for gangliosides was distinctive from that of either LT-IIa or LT-IIb. The data suggest that other types of the type II HLT subfamily are circulating in the environment and that host specificity of type II HLT is likely governed by changes in the B polypeptide which mediate binding to receptors.
Figures


References
-
- Blanco, J. E., and M. Blanco. 1993. Escherichia coli enterotoxigenicos, necrotoxigenicos y verotoxigenicos de origen humano e bovino—pathogenesis epidemiologia y diangostico microbiologico. Servicio de Publicaciones Diputacion Provincial San Marcos, Lugo, Spain.
-
- Chaudhuri, R. R., M. Sebaihia, J. L. Hobman, M. A. Webber, D. L. Leyton, M. D. Goldberg, A. F. Cunningham, A. Scott-Tucker, P. R. Ferguson, C. M. Thomas, G. Frankel, C. M. Tang, E. G. Dudley, I. S. Roberts, D. A. Rasko, M. J. Pallen, J. Parkhill, J. P. Nataro, N. R. Thomson, and I. R. Henderson. 2010. Complete genome sequence and comparative metabolic profiling of the prototypical enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strain 042. PLoS One 5:e8801. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

