Subinhibitory concentrations of protein synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics promote increased expression of the agr virulence regulator and production of phenol-soluble modulin cytolysins in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 20713669
- PMCID: PMC2976111
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00064-10
Subinhibitory concentrations of protein synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics promote increased expression of the agr virulence regulator and production of phenol-soluble modulin cytolysins in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Tetracycline, clindamycin, and other protein synthesis inhibitors at subinhibitory concentrations significantly increased the expression of the pivotal virulence regulator agr and production of the agr-regulated cytolytic phenol-soluble modulins in the community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) strain USA300. Our results suggest that such protein synthesis inhibitors may exacerbate the progression of CA-MRSA disease when applied at concentrations that are too low or when treating infections caused by strains resistant to those antibiotics.
Figures
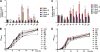
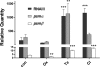
Similar articles
-
Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations of Oxacillin, but Not Clindamycin, Linezolid, or Tigecycline, Decrease Staphylococcal Phenol-Soluble Modulin Expression in Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0080821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00808-21. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35044221 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the accessory gene regulator agr in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2011 May;79(5):1927-35. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00046-11. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21402769 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing, Virulence, and Antibiotic Resistance of USA100 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates.mSphere. 2019 Aug 14;4(4):e00553-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00553-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31413175 Free PMC article.
-
Basis of virulence in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010;64:143-62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134309. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20825344 Review.
-
Beyond conventional antibiotics for the future treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: two novel alternatives.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012 Aug;65(3):399-412. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.00954.x. Epub 2012 Apr 4. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22409572 Review.
Cited by
-
Sub-Inhibitory Concentrations of Oxacillin, but Not Clindamycin, Linezolid, or Tigecycline, Decrease Staphylococcal Phenol-Soluble Modulin Expression in Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0080821. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00808-21. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35044221 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-staphylococcus Antibiotics Interfere With the Transcription of Leucocidin ED Gene in Staphylococcus aureus Strain Newman.Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 5;11:265. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00265. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32194524 Free PMC article.
-
The Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Hamamelitannin Increases Antibiotic Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms by Affecting Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis and eDNA Release.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 1;6:20321. doi: 10.1038/srep20321. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26828772 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of subinhibitory concentrations of tigecycline and ciprofloxacin on the expression of biofilm-associated genes and biofilm structure of Staphylococcus epidermidis.Microbiology (Reading). 2017 May;163(5):712-718. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000453. Epub 2017 May 9. Microbiology (Reading). 2017. PMID: 28481197 Free PMC article.
-
Concentration-Dependent Global Quantitative Proteome Response of Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A Biofilms to Subinhibitory Tigecycline.Cells. 2022 Nov 3;11(21):3488. doi: 10.3390/cells11213488. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies, J., G. B. Spiegelman, and G. Yim. 2006. The world of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9:445-453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

