Sucrose nonfermenting AMPK-related kinase (SNARK) mediates contraction-stimulated glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle
- PMID: 20713714
- PMCID: PMC2932588
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1008131107
Sucrose nonfermenting AMPK-related kinase (SNARK) mediates contraction-stimulated glucose transport in mouse skeletal muscle
Abstract
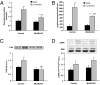
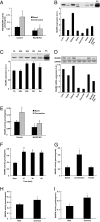
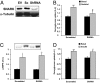
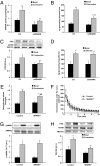
The signaling mechanisms that mediate the important effects of contraction to increase glucose transport in skeletal muscle are not well understood, but are known to occur through an insulin-independent mechanism. Muscle-specific knockout of LKB1, an upstream kinase for AMPK and AMPK-related protein kinases, significantly inhibited contraction-stimulated glucose transport. This finding, in conjunction with previous studies of ablated AMPKalpha2 activity showing no effect on contraction-stimulated glucose transport, suggests that one or more AMPK-related protein kinases are important for this process. Muscle contraction increased sucrose nonfermenting AMPK-related kinase (SNARK) activity, an effect blunted in the muscle-specific LKB1 knockout mice. Expression of a mutant SNARK in mouse tibialis anterior muscle impaired contraction-stimulated, but not insulin-stimulated, glucose transport. Whole-body SNARK heterozygotic knockout mice also had impaired contraction-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle, and knockdown of SNARK in C2C12 muscle cells impaired sorbitol-stimulated glucose transport. SNARK is activated by muscle contraction and is a unique mediator of contraction-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nesher R, Karl IE, Kipnis DM. Dissociation of effects of insulin and contraction on glucose transport in rat epitrochlearis muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985;249:C226–C232. - PubMed
-
- Wallberg-Henriksson H, Constable SH, Young DA, Holloszy JO. Glucose transport into rat skeletal muscle: Interaction between exercise and insulin. J Appl Physiol. 1988;65:909–913. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Hirshman MF, Kurth EJ, Winder WW, Goodyear LJ. Evidence for 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase mediation of the effect of muscle contraction on glucose transport. Diabetes. 1998;47:1369–1373. - PubMed
-
- Lee AD, Hansen PA, Holloszy JO. Wortmannin inhibits insulin-stimulated but not contraction-stimulated glucose transport activity in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1995;361:51–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

