Humanized nonobese diabetic-scid IL2rgammanull mice are susceptible to lethal Salmonella Typhi infection
- PMID: 20713716
- PMCID: PMC2932584
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1005566107
Humanized nonobese diabetic-scid IL2rgammanull mice are susceptible to lethal Salmonella Typhi infection
Abstract
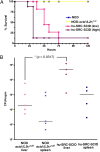
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the cause of typhoid fever, is host-adapted to humans and unable to cause disease in mice. Here, we show that S. Typhi can replicate in vivo in nonobese diabetic (NOD)-scid IL2rgamma(null) mice engrafted with human hematopoietic stem cells (hu-SRC-SCID mice) to cause a lethal infection with pathological and inflammatory cytokine responses resembling human typhoid. In contrast, S. Typhi does not exhibit net replication or cause illness in nonengrafted or immunocompetent control animals. Screening of transposon pools in hu-SRC-SCID mice revealed both known and previously unknown Salmonella virulence determinants, including Salmonella Pathogenicity Islands 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6. Our observations indicate that the presence of human immune cells allows the in vivo replication of S. Typhi in mice. The hu-SRC-SCID mouse provides an unprecedented opportunity to gain insights into S. Typhi pathogenesis and devise strategies for the prevention of typhoid fever.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Parry CM, Threlfall EJ. Antimicrobial resistance in typhoidal and nontyphoidal salmonellae. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008;21:531–538. - PubMed
-
- Guzman CA, et al. Vaccines against typhoid fever. Vaccine. 2006;24:3804–3811. - PubMed
-
- Levine MM, et al. Duration of efficacy of Ty21a, attenuated Salmonella typhi live oral vaccine. Vaccine. 1999;17(Suppl 2):S22–S27. - PubMed
-
- Corbel MJ. Reasons for instability of bacterial vaccines. Dev Biol Stand. 1996;87:113–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI048622/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI062859/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI75093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI82785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI039557/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI83646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI44486/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044486/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI16629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK032520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048622/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK32520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI039557/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI62859/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R13 AI082785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI48622/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

