Eosinophils in the zebrafish: prospective isolation, characterization, and eosinophilia induction by helminth determinants
- PMID: 20713961
- PMCID: PMC2981543
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-267419
Eosinophils in the zebrafish: prospective isolation, characterization, and eosinophilia induction by helminth determinants
Abstract
Eosinophils are granulocytic leukocytes implicated in numerous aspects of immunity and disease. The precise functions of eosinophils, however, remain enigmatic. Alternative models to study eosinophil biology may thus yield novel insights into their function. Eosinophilic cells have been observed in zebrafish but have not been thoroughly characterized. We used a gata2:eGFP transgenic animal to enable prospective isolation and characterization of zebrafish eosinophils, and demonstrate that all gata2(hi) cells in adult hematopoietic tissues are eosinophils. Although eosinophils are rare in most organs, they are readily isolated from whole kidney marrow and abundant within the peritoneal cavity. Molecular analyses demonstrate that zebrafish eosinophils express genes important for the activities of mammalian eosinophils. In addition, gata2(hi) cells degranulate in response to helminth extract. Chronic exposure to helminth- related allergens resulted in profound eosinophilia, demonstrating that eosinophil responses to allergens have been conserved over evolution. Importantly, infection of adult zebrafish with Pseudocapillaria tomentosa, a natural nematode pathogen of teleosts, caused marked increases in eosinophil number within the intestine. Together, these observations support a conserved role for eosinophils in the response to helminth antigens or infection and provide a new model to better understand how parasitic worms activate, co-opt, or evade the vertebrate immune response.
Figures
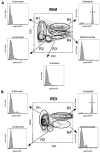
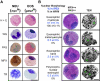



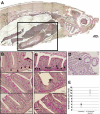
Comment in
-
Eosinophils are in the swim!Blood. 2010 Nov 11;116(19):3692-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-304345. Blood. 2010. PMID: 21071614 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hogan SP, Rosenberg HF, Moqbel R, et al. Eosinophils: biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38(5):709–750. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP. The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:147–174. - PubMed
-
- Humbles AA, Lloyd CM, McMillan SJ, et al. A critical role for eosinophils in allergic airways remodeling. Science. 2004;305(5691):1776–1779. - PubMed
-
- Lee JJ, Dimina D, Macias MP, et al. Defining a link with asthma in mice congenitally deficient in eosinophils. Science. 2004;305(5691):1773–1776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR12546/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ES011587/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES003850/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES013124/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-HL086344/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES013124/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI056189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5P30CA23100-22S2/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GMO68524/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 ES000210/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T34 GM008303/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011587/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T34GM08303/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P40 RR012546/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ES00210/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK074482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL086344/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES03850/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01DK074482-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

