Characterization of dextrins with different Dextrose Equivalents
- PMID: 20714293
- PMCID: PMC6257794
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15085162
Characterization of dextrins with different Dextrose Equivalents
Abstract
Dextrins are widely used for their functional properties and prepared by partial hydrolysis of starch using acid, enzymes, or combinations of both. The physiochemical properties of dextrins are dependent on their molecular distribution and oligosaccharide profiles. In this study, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), rapid viscoanalysis (RVA), high-performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) were used to characterize dextrins prepared by common neutral and thermostable alpha-amylase hydrolysis. The dextrin granules displayed irregular surfaces and were badly damaged by the enzyme treatment. They displayed A-type X-ray diffraction patterns with a decrease of intensity of the characteristic diffraction peaks. The RVA profiles showed that the viscosity of dextrin decreased with the increase of its Dextrose Equivalent (DE) value. According to HPLC analysis, the molecular weight, degree of polymerization and the composition of oligosaccharides in dextrins were different.
Figures

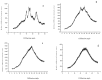

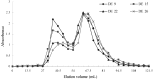


References
-
- White D.R., Jr., Hudson P., Adamson J.T. Dextrin characterization by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography-pulsed amperometric detection and size-exclusion chromatography–multi-angle light scattering-refractive index detection. J. Chromatogr. A. 2003;997:79–85. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00626-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tester R.F., Qi X., Karkalas J. Hydrolysis of native starches with amylases. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006;130:39–54. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2006.01.016. - DOI
-
- Chronakis I.S., Kasapis S., Richardson R.K. Small deformation rheological properties of maltodextrin-milk protein systems. Carbohyd. Polym. 1996;29:137–148. doi: 10.1016/0144-8617(96)00014-8. - DOI
-
- Dokik P., Jakovljevic J., Dokic-Baucal L. Molecular characteristics of maltodextrins and rheological behaviour of diluted and concentrated solutions. Colloids Surfaces A. 1998;141:435–440. doi: 10.1016/S0927-7757(97)00118-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

