Emerging biological importance of central nervous system lanthionines
- PMID: 20714314
- PMCID: PMC6257760
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15085581
Emerging biological importance of central nervous system lanthionines
Abstract
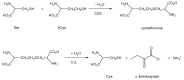
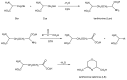
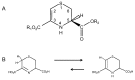
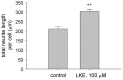
Lanthionine (Lan), the thioether analog of cystine, is a natural but nonproteogenic amino acid thought to form naturally in mammals through promiscuous reactivity of the transsulfuration enzyme cystathionine-beta-synthase (CbetaS). Lanthionine exists at appreciable concentrations in mammalian brain, where it undergoes aminotransferase conversion to yield an unusual cyclic thioether, lanthionine ketimine (LK; 2H-1,4-thiazine-5,6-dihydro-3,5-dicarboxylic acid). Recently, LK was discovered to possess neuroprotective, neuritigenic and anti-inflammatory activities. Moreover, both LK and the ubiquitous redox regulator glutathione (gamma-glutamyl-cysteine-glycine) bind to mammalian lanthionine synthetase-like protein-1 (LanCL1) protein which, along with its homolog LanCL2, has been associated with important physiological processes including signal transduction and insulin sensitization. These findings begin to suggest that Lan and its downstream metabolites may be physiologically important substances rather than mere metabolic waste. This review summarizes the current state of knowledge about lanthionyl metabolites with emphasis on their possible relationships to LanCL1/2 proteins and glutathione. The potential significance of lanthionines in paracrine signaling is discussed with reference to opportunities for utilizing bioavailable pro-drug derivatives of these compounds as novel pharmacophores.
Figures
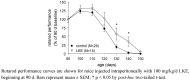
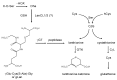
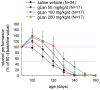
Similar articles
-
Alternative functions of the brain transsulfuration pathway represent an underappreciated aspect of brain redox biochemistry with significant potential for therapeutic engagement.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jan;78:123-34. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.10.581. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25463282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis of Hydrogen Sulfide and Thioethers by Cystathionine Beta-Synthase.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Feb 1;28(4):311-323. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7009. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28874062
-
LanCL proteins are not Involved in Lanthionine Synthesis in Mammals.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 20;7:40980. doi: 10.1038/srep40980. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28106097 Free PMC article.
-
Thioethers as markers of hydrogen sulfide production in homocystinurias.Biochimie. 2016 Jul;126:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26791043
-
Progress in Lanthionine and Protected Lanthionine Synthesis.Chemistry. 2018 Oct 17;24(58):15421-15441. doi: 10.1002/chem.201801115. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29714402 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in therapy development for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Neurol Res Int. 2012;2012:187234. doi: 10.1155/2012/187234. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Neurol Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22830014 Free PMC article.
-
Moving towards effective therapeutic strategies for Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016 Apr 16;11:40. doi: 10.1186/s13023-016-0414-2. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016. PMID: 27083890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple-step, one-pot synthesis of 2-substituted-3-phosphono-1-thia-4-aza-2-cyclohexene-5-carboxylates and their corresponding ethyl esters.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Feb 15;28(4):562-565. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.01.052. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 29398540 Free PMC article.
-
Opening Pandora's jar: a primer on the putative roles of CRMP2 in a panoply of neurodegenerative, sensory and motor neuron, and central disorders.Future Neurol. 2012 Nov 1;7(6):749-771. doi: 10.2217/FNL.12.68. Future Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23308041 Free PMC article.
-
Expanded natural product diversity revealed by analysis of lanthipeptide-like gene clusters in actinobacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Jul;81(13):4339-50. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00635-15. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25888176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pryor W.A., editor. Mechanism of Sulfur Reactions. McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc; New York, NY, USA: 1962.
-
- Mitchell S.C., editor. Biological Interactions of Sulfur Compounds. Taylor and Francis Publishers; Bristol, PA, USA: 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

