Functions of disordered regions in mammalian early base excision repair proteins
- PMID: 20714778
- PMCID: PMC2996047
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0485-5
Functions of disordered regions in mammalian early base excision repair proteins
Abstract
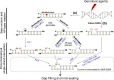
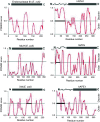
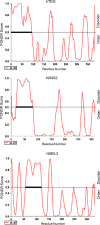
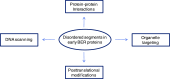
Reactive oxygen species, generated endogenously and induced as a toxic response, produce several dozen oxidized or modified bases and/or single-strand breaks in mammalian and other genomes. These lesions are predominantly repaired via the conserved base excision repair (BER) pathway. BER is initiated with excision of oxidized or modified bases by DNA glycosylases leading to formation of abasic (AP) site or strand break at the lesion site. Structural analysis by experimental and modeling approaches shows the presence of a disordered segment commonly localized at the N- or C-terminus as a characteristic signature of mammalian DNA glycosylases which is absent in their bacterial prototypes. Recent studies on unstructured regions in DNA metabolizing proteins have indicated their essential role in interaction with other proteins and target DNA recognition. In this review, we have discussed the unique presence of disordered segments in human DNA glycosylases, and AP endonuclease involved in the processing of glycosylase products, and their critical role in regulating repair functions. These disordered segments also include sites for posttranslational modifications and nuclear localization signal. The teleological basis for their structural flexibility is discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oxidized base damage and single-strand break repair in mammalian genomes: role of disordered regions and posttranslational modifications in early enzymes.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;110:123-53. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387665-2.00006-7. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22749145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early steps in the DNA base excision/single-strand interruption repair pathway in mammalian cells.Cell Res. 2008 Jan;18(1):27-47. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.8. Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18166975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative DNA damage repair in mammalian cells: a new perspective.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Apr 1;6(4):470-80. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.10.011. Epub 2006 Nov 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17116430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A short review on the implications of base excision repair pathway for neurons: relevance to neurodegenerative diseases.Mitochondrion. 2014 May;16:38-49. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2013.10.007. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Mitochondrion. 2014. PMID: 24220222 Review.
-
Long patch base excision repair in mammalian mitochondrial genomes.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 26;283(39):26349-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803491200. Epub 2008 Jul 17. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18635552 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lighting up Nobel Prize-winning studies with protein intrinsic disorder.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 26;79(8):449. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04468-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35882686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Base excision repair.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Apr 1;5(4):a012583. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012583. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23545420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New paradigms in the repair of oxidative damage in human genome: mechanisms ensuring repair of mutagenic base lesions during replication and involvement of accessory proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 May;72(9):1679-98. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1820-z. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25575562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Describing sequence-ensemble relationships for intrinsically disordered proteins.Biochem J. 2013 Jan 15;449(2):307-18. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121346. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23240611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel interaction interfaces mediate the interaction between the NEIL1 DNA glycosylase and mitochondrial transcription factor A.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 22;10:893806. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.893806. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35938152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitra S, Hazra TK, Roy R, Ikeda S, Biswas T, Lock J, Boldogh I, Izumi T. Complexities of DNA base excision repair in mammalian cells. Mol Cells. 1997;7:305–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

