CD36-mediated activation of endothelial cell apoptosis by an N-terminal recombinant fragment of thrombospondin-2 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo
- PMID: 20714802
- PMCID: PMC3291836
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-010-1085-7
CD36-mediated activation of endothelial cell apoptosis by an N-terminal recombinant fragment of thrombospondin-2 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo
Abstract
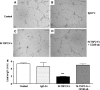
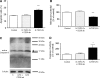
Thus far the clinical benefits seen in breast cancer patients treated with drugs targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway are only modest. Consequently, additional antiangiogenic approaches for treatment of breast cancer need to be investigated. Thrombospondin-2 (TSP-2) has been shown to inhibit tumor growth and angiogenesis with a greater potency than the related molecule TSP-1. The systemic effects of TSP-2 on tumor metastasis and the underlying molecular mechanisms of the antiangiogenic activity of TSP-2 have remained poorly understood. We generated a recombinant fusion protein consisting of the N-terminal region of TSP-2 and the IgG-Fc1 fragment (N-TSP2-Fc) and could demonstrate that the antiangiogenic activity of N-TSP2-Fc is dependent on the CD36 receptor. We found that N-TSP2-Fc inhibited VEGF-induced tube formation of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) on matrigel in vitro and that concurrent incubation of anti-CD36 antibody with N-TSP2-Fc resulted in tube formation that was comparable to untreated control. N-TSP2-Fc potently induced apoptosis of HDMEC in vitro in a CD36-dependent manner. Moreover, we could demonstrate a CD36 receptor-mediated loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and activation of caspase-3 in HDMEC in vitro. Daily intraperitoneal injections of N-TSP2-Fc resulted in a significant inhibition of the growth of human MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-231 tumor cells grown in the mammary gland of immunodeficient nude mice and in reduced tumor vascularization. Finally, increased serum concentrations of N-TSP2-Fc significantly inhibited regional metastasis to lymph nodes and distant metastasis to lung as shown by quantitative real-time alu PCR. These results identify N-TSP2-Fc as a potent systemic inhibitor of tumor metastasis and provide strong evidence for an important role of the CD36 receptor in mediating the antiangiogenic activity of TSP-2.
Figures

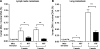
Similar articles
-
An N-terminal 80 kDa recombinant fragment of human thrombospondin-2 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor induced endothelial cell migration in vitro and tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo.J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Dec;121(6):1536-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12643.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 14675207
-
Inhibition of tumor growth by systemic treatment with thrombospondin-1 peptide mimetics.Int J Cancer. 2002 Apr 10;98(5):682-9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10247. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11920636
-
CD36 mediates the In vitro inhibitory effects of thrombospondin-1 on endothelial cells.J Cell Biol. 1997 Aug 11;138(3):707-17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.3.707. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9245797 Free PMC article.
-
CD36-TSP-HRGP interactions in the regulation of angiogenesis.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(35):3559-67. doi: 10.2174/138161207782794185. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 18220792 Review.
-
Thrombospondins and tumor angiogenesis.Trends Mol Med. 2001 Sep;7(9):401-7. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4914(01)02102-5. Trends Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11530335 Review.
Cited by
-
Scavenger Receptors: Emerging Roles in Cancer Biology and Immunology.Adv Cancer Res. 2015;128:309-64. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Adv Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26216637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Aug 12;13(4):215. doi: 10.1186/bcr2889. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21884641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defects in tendon, ligament, and enthesis in response to genetic alterations in key proteoglycans and glycoproteins: a review.Arthritis. 2013;2013:154812. doi: 10.1155/2013/154812. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Arthritis. 2013. PMID: 24324885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombospondin 1 Triggers Osteosarcoma Cell Metastasis and Tumor Angiogenesis.Oncol Res. 2019 Feb 5;27(2):211-218. doi: 10.3727/096504018X15208993118389. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 29540257 Free PMC article.
-
THBS2, a microRNA-744-5p target, modulates MMP9 expression through CUX1 in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.Oncol Lett. 2020 Mar;19(3):1683-1692. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11273. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32194660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnoletti JP, Albo D, Granick MS, Solomon MP, Castiglioni A, Rothman VL, Tuszynski GP. Thrombospondin and transforming growth factor-beta 1 increase expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer. 1995;76:998–1005. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950915)76:6<998::AID-CNCR2820760613>3.0.CO;2-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

