Sequential depletion and acquisition of proteins during Golgi stack disassembly and reformation
- PMID: 20716110
- PMCID: PMC3039244
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01106.x
Sequential depletion and acquisition of proteins during Golgi stack disassembly and reformation
Abstract
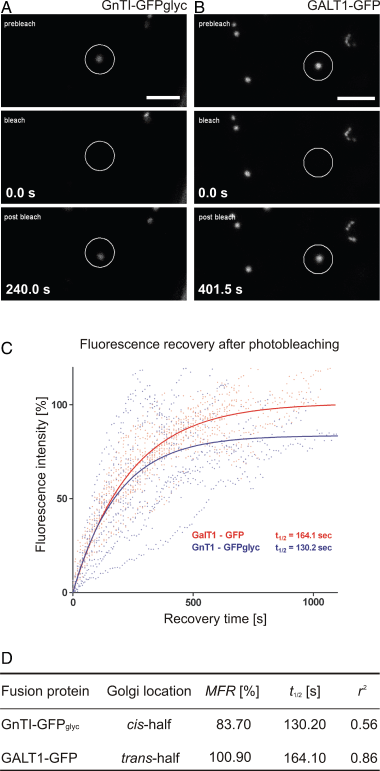
Herein, we report the stepwise transport of multiple plant Golgi membrane markers during disassembly of the Golgi apparatus in tobacco leaf epidermal cells in response to the induced expression of the GTP-locked Sar1p or Brefeldin A (BFA), and reassembly on BFA washout. The distribution of fluorescent Golgi-resident N-glycan processing enzymes and matrix proteins (golgins) with specific cis-trans-Golgi sub-locations was followed by confocal microscopy during disassembly and reassembly. The first event during Golgi disassembly was the loss of trans-Golgi enzymes and golgins from Golgi membranes, followed by a sequential redistribution of medial and cis-Golgi enzymes into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), whilst golgins were relocated to the ER or cytoplasm. This event was confirmed by fractionation and immuno-blotting. The sequential redistribution of Golgi components in a trans-cis sequence may highlight a novel retrograde trafficking pathway between the trans-Golgi and the ER in plants. Release of Golgi markers from the ER upon BFA washout occurred in the opposite sequence, with cis-matrix proteins labelling Golgi-like structures before cis/medial enzymes. Trans-enzyme location was preceded by trans-matrix proteins being recruited back to Golgi membranes. Our results show that Golgi disassembly and reassembly occur in a highly ordered fashion in plants.
© 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures
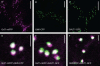
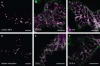
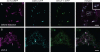
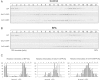


Similar articles
-
Sub-compartmental organization of Golgi-resident N-glycan processing enzymes in plants.Mol Plant. 2011 Mar;4(2):220-8. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq082. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Mol Plant. 2011. PMID: 21307368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reevaluation of the effects of brefeldin A on plant cells using tobacco Bright Yellow 2 cells expressing Golgi-targeted green fluorescent protein and COPI antisera.Plant Cell. 2002 Jan;14(1):237-61. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010237. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 11826310 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi regeneration after brefeldin A treatment in BY-2 cells entails stack enlargement and cisternal growth followed by division.Plant Physiol. 2007 Oct;145(2):527-38. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.104919. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17704232 Free PMC article.
-
cis-Golgi proteins accumulate near the ER exit sites and act as the scaffold for Golgi regeneration after brefeldin A treatment in tobacco BY-2 cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Aug;23(16):3203-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0034. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22740633 Free PMC article.
-
Brefeldin A effects in plant and fungal cells: something new about vesicle trafficking?J Microsc. 1996 Feb;181(Pt 2):162-77. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.1996.112393.x. J Microsc. 1996. PMID: 8919983 Review.
Cited by
-
ER Import Sites and Their Relationship to ER Exit Sites: A New Model for Bidirectional ER-Golgi Transport in Higher Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Jul 2;3:143. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00143. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22876251 Free PMC article.
-
Is the 6 kDa tobacco etch viral protein a bona fide ERES marker?J Exp Bot. 2011 Oct;62(14):5013-23. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err200. Epub 2011 Jun 24. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21705387 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-compartmental organization of Golgi-resident N-glycan processing enzymes in plants.Mol Plant. 2011 Mar;4(2):220-8. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq082. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Mol Plant. 2011. PMID: 21307368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Models for Golgi traffic: a critical assessment.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Nov 1;3(11):a005215. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005215. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21875986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tobacco GNTI stem region harbors a strong motif for homomeric protein complex formation.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Nov 28;14:1320051. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1320051. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38089803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hawes C, Osterrieder A, Hummel E, Sparkes I. The plant ER-Golgi interface. Traffic. 2008;9:1571–1580.. - PubMed
-
- Faso C, Boulaflous A, Brandizzi F. The plant Golgi apparatus: last 10 years of answered and open questions. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:3752–3757.. - PubMed
-
- Robinson D, Langhans M, Saint-Jore-Dupas C, Hawes C. BFA effects are tissue and not just plant specific. Trends Plant Sci. 2008;13:405–408.. - PubMed
-
- Sparkes I, Ketelaar T, de Ruijter N, Hawes C. Grab a Golgi: laser trapping of Golgi bodies reveals in vivo interactions with the endoplasmic reticulum. Traffic. 2009;10:567–571.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

