Cutting edge: Chk1 directs senescence and mitotic catastrophe in recovery from G₂ checkpoint arrest
- PMID: 20716119
- PMCID: PMC3823197
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01143.x
Cutting edge: Chk1 directs senescence and mitotic catastrophe in recovery from G₂ checkpoint arrest
Abstract
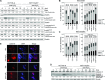
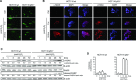
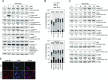
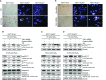
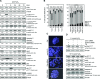
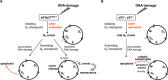
Besides the well-understood DNA damage response via establishment of G(2) checkpoint arrest, novel studies focus on the recovery from arrest by checkpoint override to monitor cell cycle re-entry. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of Chk1 in the recovery from G(2) checkpoint arrest in HCT116 (human colorectal cancer) wt, p53(-/-) and p21(-/-) cell lines following H(2) O(2) treatment. Firstly, DNA damage caused G(2) checkpoint activation via Chk1. Secondly, overriding G(2) checkpoint led to (i) mitotic slippage, cell cycle re-entry in G(1) and subsequent G(1) arrest associated with senescence or (ii) premature mitotic entry in the absence of p53/p21(WAF1) causing mitotic catastrophe. We revealed subtle differences in the initial Chk1-involved G(2) arrest with respect to p53/p21(WAF1) : absence of either protein led to late G(2) arrest instead of the classic G(2) arrest during checkpoint initiation, and this impacted the release back into the cell cycle. Thus, G(2) arrest correlated with downstream senescence, but late G(2) arrest led to mitotic catastrophe, although both cell cycle re-entries were linked to upstream Chk1 signalling. Chk1 knockdown deciphered that Chk1 defines long-term DNA damage responses causing cell cycle re-entry. We propose that recovery from oxidative DNA damage-induced G(2) arrest requires Chk1. It works as cutting edge and navigates cells to senescence or mitotic catastrophe. The decision, however, seems to depend on p53/p21(WAF1) . The general relevance of Chk1 as an important determinant of recovery from G(2) checkpoint arrest was verified in HT29 colorectal cancer cells.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chk1 is dispensable for G2 arrest in response to sustained DNA damage when the ATM/p53/p21 pathway is functional.Oncogene. 2011 Oct 13;30(41):4261-74. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.135. Epub 2011 May 2. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21532626
-
Defective p53 signaling in p53 wild-type tumors attenuates p21waf1 induction and cyclin B repression rendering them sensitive to Chk1 inhibitors that abrogate DNA damage-induced S and G2 arrest.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Feb;7(2):252-62. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2066. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18281511
-
Abrogation of the Chk1-mediated G(2) checkpoint pathway potentiates temozolomide-induced toxicity in a p53-independent manner in human glioblastoma cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Aug 1;61(15):5843-9. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11479224
-
Turning off the G2 DNA damage checkpoint.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Feb 1;7(2):136-40. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.07.017. Epub 2007 Sep 11. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 17851138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Death by releasing the breaks: CHK1 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics.Trends Mol Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.10.009. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Trends Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21087899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogenous Differences in Cellular Senescent Phenotypes in Pre-Eclampsia and IUGR following Quantitative Assessment of Multiple Biomarkers of Senescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3101. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043101. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834513 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage signaling induced by the G-quadruplex ligand 12459 is modulated by PPM1D/WIP1 phosphatase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr 1;41(6):3588-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt073. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23396447 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced cellular senescence results from a slippage of long-term G2 arrested cells into G1 phase.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 1;12(9):1424-32. doi: 10.4161/cc.24528. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23574719 Free PMC article.
-
A novel M phase blocker, DCZ3301 enhances the sensitivity of bortezomib in resistant multiple myeloma through DNA damage and mitotic catastrophe.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 9;39(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01597-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32517809 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the SLC25A1 gene during embryogenesis induces a unique senescence program controlled by p53.Cell Death Differ. 2025 May;32(5):818-836. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01428-w. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 39733217 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

