Macrophages, reactive nitrogen species, and lung injury
- PMID: 20716284
- PMCID: PMC3797654
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05607.x
Macrophages, reactive nitrogen species, and lung injury
Abstract
Evidence has accumulated over the past several years demonstrating that lung injury following inhalation of irritants like ozone is due, not only to direct effects of the chemical, but also indirectly to the actions of inflammatory mediators released by infiltrating macrophages. Among the mediators involved in the cytotoxic process, reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are of particular interest because of their well-documented cytotoxic potential. Findings that macrophage suppression blocks RNS production and ozone-induced toxicity provide strong support for a role of these cells and inflammatory mediators in lung injury. Recent investigations have focused on understanding pathways by which macrophages become activated to release RNS. One protein that has attracted considerable attention is caveolin-1, a membrane scaffolding molecule that functions to negatively regulate cell signaling. The fact that expression of caveolin-1 is down-regulated in macrophages after ozone inhalation suggests a mechanism controlling the release of cytotoxic mediators by these inflammatory cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
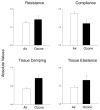
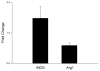

References
-
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Air quality criteria for ozone and related oxidants 2005
-
- Levy JI, Chemerynski SM, Sarnat JA. Ozone exposure and mortality: an empiric Bayes metaregression analysis. Epidemiology. 2005;16:458–468. - PubMed
-
- Dale DC, Boxer L, Liles WC. The phagocytes: neutrophils and monocytes. Blood. 2008;112:935–945. - PubMed
-
- Laskin DL, Laskin JD. Role of macrophages and inflammatory mediators in chemically induced toxicity. Toxicology. 2001;160:111–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA132624/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086621/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR055073/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007148/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL086621/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005022/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA13264/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM034310/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AR055073/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ES005022/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- GM034310/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ES004738/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES004738/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

