Archaeal/eukaryal RNase P: subunits, functions and RNA diversification
- PMID: 20716516
- PMCID: PMC3001073
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq701
Archaeal/eukaryal RNase P: subunits, functions and RNA diversification
Abstract
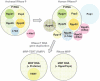
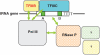
RNase P, a catalytic ribonucleoprotein (RNP), is best known for its role in precursor tRNA processing. Recent discoveries have revealed that eukaryal RNase P is also required for transcription and processing of select non-coding RNAs, thus enmeshing RNase P in an intricate network of machineries required for gene expression. Moreover, the RNase P RNA seems to have been subject to gene duplication, selection and divergence to generate two new catalytic RNPs, RNase MRP and MRP-TERT, which perform novel functions encompassing cell cycle control and stem cell biology. We present new evidence and perspectives on the functional diversification of the RNase P RNA to highlight it as a paradigm for the evolutionary plasticity that underlies the extant broad repertoire of catalytic and unexpected regulatory roles played by RNA-driven RNPs.
Figures

References
-
- Altman S, Smith JD. Tyrosine tRNA precursor molecule polynucleotide sequence. Nature. 1971;233:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Robertson HD, Altman S, Smith JD. Purification and properties of a specific Escherichia coli ribonuclease which cleaves a tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid presursor. J. Biol. Chem. 1972;247:5243–5251. - PubMed
-
- Kole R, Baer MF, Stark BC, Altman S. E. coli RNase P has a required RNA component. Cell. 1980;19:881–887. - PubMed
-
- Gardiner K, Pace NR. RNase P of Bacillus subtilis has a RNA component. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:7507–7509. - PubMed

