Editing of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BART6 microRNAs controls their dicer targeting and consequently affects viral latency
- PMID: 20716523
- PMCID: PMC2963350
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.138362
Editing of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BART6 microRNAs controls their dicer targeting and consequently affects viral latency
Abstract
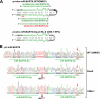
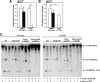
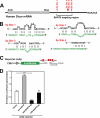
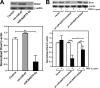
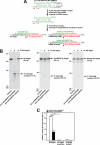
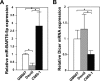
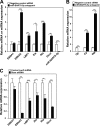
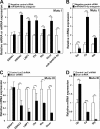
Certain primary transcripts of miRNA (pri-microRNAs) undergo RNA editing that converts adenosine to inosine. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome encodes multiple microRNA genes of its own. Here we report that primary transcripts of ebv-miR-BART6 (pri-miR-BART6) are edited in latently EBV-infected cells. Editing of wild-type pri-miR-BART6 RNAs dramatically reduced loading of miR-BART6-5p RNAs onto the microRNA-induced silencing complex. Editing of a mutation-containing pri-miR-BART6 found in Daudi Burkitt lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma C666-1 cell lines suppressed processing of miR-BART6 RNAs. Most importantly, miR-BART6-5p RNAs silence Dicer through multiple target sites located in the 3'-UTR of Dicer mRNA. The significance of miR-BART6 was further investigated in cells in various stages of latency. We found that miR-BART6-5p RNAs suppress the EBNA2 viral oncogene required for transition from immunologically less responsive type I and type II latency to the more immunoreactive type III latency as well as Zta and Rta viral proteins essential for lytic replication, revealing the regulatory function of miR-BART6 in EBV infection and latency. Mutation and A-to-I editing appear to be adaptive mechanisms that antagonize miR-BART6 activities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p stabilizes Epstein-Barr virus latency by directly targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9027-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00721-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899173 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbation of biogenesis and targeting of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART3 microRNA by adenosine-to-inosine editing.J Gen Virol. 2013 Dec;94(Pt 12):2739-2744. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.056226-0. Epub 2013 Sep 17. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 24045110
-
Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein regulates viral latency through effects on let-7 microRNA and dicer.J Virol. 2014 Oct;88(19):11166-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01785-14. Epub 2014 Jul 16. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25031339 Free PMC article.
-
A review on EBV encoded and EBV-induced host microRNAs expression profile in different lymphoma types.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Feb;48(2):1801-1817. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06152-z. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33523370 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jan 23;47(1):e131. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.84. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25613728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Targets for Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs in B Cell Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;16(20):3537. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203537. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456631 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR1 forms a complex with Dicer to promote microRNA processing and RNA-induced gene silencing.Cell. 2013 Apr 25;153(3):575-89. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.024. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23622242 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART15-3p promotes cell apoptosis partially by targeting BRUCE.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(14):8135-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03159-12. Epub 2013 May 15. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23678170 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs as regulators in host immune responses.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Apr 5;14(5):565-576. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24562. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29805308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple functions are mediated by the miRNAs of Epstein-Barr virus.Curr Opin Virol. 2014 Aug;7:61-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 May 10. Curr Opin Virol. 2014. PMID: 24814666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel D. P. (2004) Cell 116, 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Stefani G., Slack F. J. (2008) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 219–230 - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A., Slack F. J. (2006) Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 259–269 - PubMed
-
- Kim V. N., Han J., Siomi M. C. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 126–139 - PubMed
-
- Winter J., Jung S., Keller S., Gregory R. I., Diederichs S. (2009) Nat. Cell Biol. 11, 228–234 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

