Regulation of the AGS3·G{alpha}i signaling complex by a seven-transmembrane span receptor
- PMID: 20716524
- PMCID: PMC2962495
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.138073
Regulation of the AGS3·G{alpha}i signaling complex by a seven-transmembrane span receptor
Abstract
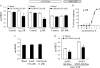
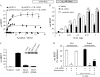
G-protein signaling modulators (GPSM) play diverse functional roles through their interaction with G-protein subunits. AGS3 (GPSM1) contains four G-protein regulatory motifs (GPR) that directly bind Gα(i) free of Gβγ providing an unusual scaffold for the "G-switch" and signaling complexes, but the mechanism by which signals track into this scaffold are not well understood. We report the regulation of the AGS3·Gα(i) signaling module by a cell surface, seven-transmembrane receptor. AGS3 and Gα(i1) tagged with Renilla luciferase or yellow fluorescent protein expressed in mammalian cells exhibited saturable, specific bioluminescence resonance energy transfer indicating complex formation in the cell. Activation of α(2)-adrenergic receptors or μ-opioid receptors reduced AGS3-RLuc·Gα(i1)-YFP energy transfer by over 30%. The agonist-mediated effects were inhibited by pertussis toxin and co-expression of RGS4, but were not altered by Gβγ sequestration with the carboxyl terminus of GRK2. Gα(i)-dependent and agonist-sensitive bioluminescence resonance energy transfer was also observed between AGS3 and cell-surface receptors typically coupled to Gα(i) and/or Gα(o) indicating that AGS3 is part of a larger signaling complex. Upon receptor activation, AGS3 reversibly dissociates from this complex at the cell cortex. Receptor coupling to both Gαβγ and GPR-Gα(i) offer additional flexibility for systems to respond and adapt to challenges and orchestrate complex behaviors.
Figures






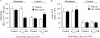
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the G-protein regulatory-Gαi signaling complex by nonreceptor guanine nucleotide exchange factors.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3003-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418467. Epub 2012 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23212907 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Coupling of a Seven-Transmembrane-Span Receptor to a Gαi G-Protein Regulatory Motif Complex.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Aug;88(2):231-7. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.097741. Epub 2015 May 13. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25972449 Free PMC article.
-
Selective interaction of AGS3 with G-proteins and the influence of AGS3 on the activation state of G-proteins.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 12;276(2):1585-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005291200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11042168
-
The Roles of Gβγ and Gα in Gating and Regulation of GIRK Channels.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015;123:27-85. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26422982 Review.
-
Sf9 cells: a versatile model system to investigate the pharmacological properties of G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;128(3):387-418. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20705094 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct detection of endogenous Gαi activity in cells with a sensitive conformational biosensor.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 22:2024.08.21.609006. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.21.609006. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229046 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
G protein-coupled receptors and resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase-8A (Ric-8A) both regulate the regulator of g protein signaling 14 RGS14·Gαi1 complex in live cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38659-38669. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274928. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21880739 Free PMC article.
-
G Protein-coupled receptor kinase-6 interacts with activator of G protein signaling-3 to regulate CXCR2-mediated cellular functions.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 1;192(5):2186-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301875. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24510965 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of G protein α (Gα) signaling by the regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14).J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 3;290(14):9037-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.634329. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25666614 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and function of the regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14)·H-Ras signaling complex in live cells are regulated by Gαi1 and Gαi-linked G protein-coupled receptors.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3620-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.440057. Epub 2012 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23250758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sato M., Blumer J. B., Simon V., Lanier S. M. (2006) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 46, 151–187 - PubMed
-
- Takesono A., Cismowski M. J., Ribas C., Bernard M., Chung P., Hazard S., 3rd, Duzic E., Lanier S. M. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33202–33205 - PubMed
-
- Cismowski M. J., Takesono A., Ma C., Lizano J. S., Xie X., Fuernkranz H., Lanier S. M., Duzic E. (1999) Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 878–883 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

