Morphine regulates dopaminergic neuron differentiation via miR-133b
- PMID: 20716624
- PMCID: PMC2981367
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.110.066837
Morphine regulates dopaminergic neuron differentiation via miR-133b
Abstract
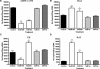
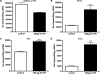
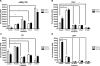
Morphine is one of the analgesics used most to treat chronic pain, although its long-term administration produces tolerance and dependence through neuronal plasticity. The ability of morphine to regulate neuron differentiation in vivo has been reported. However, the detailed mechanisms have not yet been elucidated because of the inability to separate maternal influences from embryonic events. Using zebrafish embryos as the model, we demonstrate that morphine decreases miR-133b expression, hence increasing the expression of its target, Pitx3, a transcription factor that activates tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine transporter. Using a specific morpholino to knock down the zebrafish μ-opioid receptor (zfMOR) in the embryos and selective mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors, we demonstrate that the morphine-induced miR-133b decrease in zebrafish embryos is mediated by zfMOR activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. A parallel morphine-induced down-regulation of miR-133b was observed in the immature but not in mature rat hippocampal neurons. Our results indicate for the first time that zebrafish embryos express a functional μ-opioid receptor and that zebrafish serves as an excellent model to investigate the roles of microRNA in neuronal development affected by long-term morphine exposure.
Figures
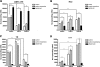
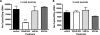
References
-
- Alvarez FA, Rodriguez-Martin I, Gonzalez-Nuñez V, de Velasco EM, Gonzalez Sarmiento R, Rodríguez RE. (2006) New kappa opioid receptor from zebrafish Danio rerio. Neurosci Lett 405:94–99 - PubMed
-
- Barrallo A, González-Sarmiento R, Alvar F, Rodríguez RE. (2000) ZFOR2, a new opioid receptor-like gene from the teleost zebrafish (Danio rerio). Brain Res Mol Brain Res 84:1–6 - PubMed
-
- Bonauer A, Carmona G, Iwasaki M, Mione M, Koyanagi M, Fischer A, Burchfield J, Fox H, Doebele C, Ohtani K, et al. (2009) MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science 324:1710–1713 - PubMed
-
- Brailoiu E, Hoard J, Brailoiu GC, Chi M, Godbolde R, Dun NJ. (2004) Ultra low concentrations of morphine increase neurite outgrowth in cultured rat spinal cord and cerebral cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 365:10–13 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

