cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action
- PMID: 20716671
- PMCID: PMC2964902
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.110.002907
cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action
Abstract
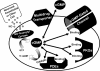
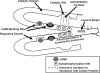
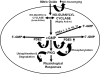
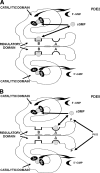
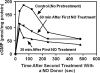
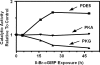
To date, studies suggest that biological signaling by nitric oxide (NO) is primarily mediated by cGMP, which is synthesized by NO-activated guanylyl cyclases and broken down by cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs). Effects of cGMP occur through three main groups of cellular targets: cGMP-dependent protein kinases (PKGs), cGMP-gated cation channels, and PDEs. cGMP binding activates PKG, which phosphorylates serines and threonines on many cellular proteins, frequently resulting in changes in activity or function, subcellular localization, or regulatory features. The proteins that are so modified by PKG commonly regulate calcium homeostasis, calcium sensitivity of cellular proteins, platelet activation and adhesion, smooth muscle contraction, cardiac function, gene expression, feedback of the NO-signaling pathway, and other processes. Current therapies that have successfully targeted the NO-signaling pathway include nitrovasodilators (nitroglycerin), PDE5 inhibitors [sildenafil (Viagra and Revatio), vardenafil (Levitra), and tadalafil (Cialis and Adcirca)] for treatment of a number of vascular diseases including angina pectoris, erectile dysfunction, and pulmonary hypertension; the PDE3 inhibitors [cilostazol (Pletal) and milrinone (Primacor)] are used for treatment of intermittent claudication and acute heart failure, respectively. Potential for use of these medications in the treatment of other maladies continues to emerge.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad F, Cong LN, Stenson Holst L, Wang LM, Rahn Landstrom T, Pierce JH, Quon MJ, Degerman E, Manganiello VC. (2000) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B is a downstream target of protein kinase B and may be involved in regulation of effects of protein kinase B on thymidine incorporation in FDCP2 cells. J Immunol 164:4678–4688 - PubMed
-
- Aitken A, Bilham T, Cohen P, Aswad D, Greengard P. (1981) A specific substrate from rabbit cerebellum for guanosine-3′:5′- monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. III. Amino acid sequences at the two phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem 256:3501–3506 - PubMed
-
- Aitken A, Hemmings BA, Hofmann F. (1984) Identification of the residues on cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase that are autophosphorylated in the presence of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta 790:219–225 - PubMed
-
- Aizawa T, Wei H, Miano JM, Abe J, Berk BC, Yan C. (2003) Role of phosphodiesterase 3 in NO/cGMP-mediated antiinflammatory effects in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 93:406–413 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

