Structural, chemical and biological aspects of antioxidants for strategies against metal and metalloid exposure
- PMID: 20716905
- PMCID: PMC2763257
- DOI: 10.4161/oxim.2.4.9112
Structural, chemical and biological aspects of antioxidants for strategies against metal and metalloid exposure
Abstract
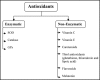
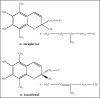
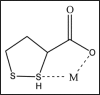
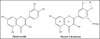
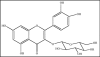
Oxidative stress contributes to the pathophysiology of exposure to heavy metals/metalloid. Beneficial renal effects of some medications, such as chelation therapy depend at least partially on the ability to alleviate oxidative stress. The administration of various natural or synthetic antioxidants has been shown to be of benefit in the prevention and attenuation of metal induced biochemical alterations. These include vitamins, N-acetylcysteine, alpha-lipoic acid, melatonin, dietary flavonoids and many others. Human studies are limited in this regard. Under certain conditions, surprisingly, the antioxidant supplements may exhibit pro-oxidant properties and even worsen metal induced toxic damage. To date, the evidence is insufficient to recommend antioxidant supplements in subject with exposure to metals. Prospective, controlled clinical trials on safety and effectiveness of different therapeutic antioxidant strategies either individually or in combination with chelating agent are indispensable. The present review focuses on structural, chemical and biological aspects of antioxidants particularly related to their chelating properties.
Figures




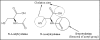


References
-
- Bargagli R. Trace metals in Antarctica related to climate change and increasing human impact. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000;166:129–173. - PubMed
-
- Mishra D, Mehta A, Flora SJS. Reversal of hepatic apoptosis with combined administration of DMSA and its analogues in guinea pigs: role of glutathione and linked enzymes. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21:400–407. - PubMed
-
- Flora SJS, Saxena G, Mehta A. Reversal of lead-induced neuronal apoptosis by chelation treatment in rats: role of ROS and intracellular Ca2+ J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;322:108–116. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Henmi K, Ogawa K, Suzuki T. Cadmium dependent generation of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial DNA breaks in photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic strains of Euglena gracilis. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol. 2003;134:227–234. - PubMed
-
- Dayan AD, Paine AJ. Mechanisms of chromium toxicity, carcinogenicity and allergenicity: review of the literature from 1985 to 2000. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2001;20:439–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

