Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease
- PMID: 20716914
- PMCID: PMC2835915
- DOI: 10.4161/oxim.2.5.9498
Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease
Abstract
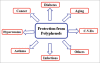
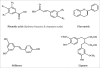
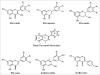
Polyphenols are secondary metabolites of plants and are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens. In the last decade, there has been much interest in the potential health benefits of dietary plant polyphenols as antioxidant. Epidemiological studies and associated meta-analyses strongly suggest that long term consumption of diets rich in plant polyphenols offer protection against development of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, osteoporosis and neurodegenerative diseases. Here we present knowledge about the biological effects of plant polyphenols in the context of relevance to human health.
Figures
References
-
- Scalbert A, Manach C, Morand C, Remesy C. Dietary polyphenols and the prevention of diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2005;45:287–306. - PubMed
-
- Spencer JP, Abd El Mohsen MM, Minihane AM, Mathers JC. Biomarkers of the intake of dietary polyphenols: strengths, limitations and application in nutrition research. Br J Nutr. 2008;99:12–22. - PubMed
-
- Beckman CH. Phenolic-storing cells: keys to programmed cell death and periderm formation in wilt disease resistance and in general defence responses in plants? Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2000;57:101–110.
-
- Graf BA, Milbury PE, Blumberg JB. Flavonols, flavonones, flavanones and human health: Epidemological evidence. J Med Food. 2005;8:281–290. - PubMed
-
- Arts ICW, Hollman PCH. Polyphenols and disease risk in epidemiologic studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81:317–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

