Prodrug and conjugate drug delivery strategies for improving HIV/AIDS therapy
- PMID: 20717488
- PMCID: PMC2921722
- DOI: 10.1016/s1773-2247(09)50001-9
Prodrug and conjugate drug delivery strategies for improving HIV/AIDS therapy
Abstract
Despite the wide variety of highly potent anti-HIV drugs that have been developed and made available in clinical practice over the years, eradication of HIV infection has not been achieved. Currently, HIV infection and AIDS are thought to be chronically treatable. HIV attacks host immune cells namely macrophages and CD4(+)T-cells and sequesters itself into sanctuary and reservoir sites such as the lymphoid tissues, testes, and brain. Initial drug delivery efforts with prodrugs and drug conjugates focused on improving the physicochemical (i.e. solubility), biopharmaceutic (i.e. absorption, metabolism), and pharmacokinetic (i.e. blood concentrations) properties of the parent drugs. Eradicating HIV, however, will require advanced drug delivery approaches in order to access and maintain effective drug concentrations for prolonged periods of time in sanctuary sites. The current review discusses prodrug/conjugate efforts, clinical successes and describes drug delivery challenges and approaches for eradicating HIV infection.
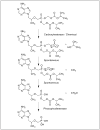
Figures

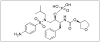

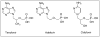
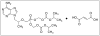
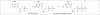




References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS and The World Health Organization-2007. AIDS epidemic update. 2007. [Accessed[June 11, 2008]]. http://www.unaids.org/en/KnowledgeCentre/Resources/Publications/-2007_ep....
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS and The World Health Organization. 2006 report on the global AIDS epidemic. 2006. [[June 11, 2008]]. http://www.unaids.org/en/KnowledgeCentre/Resources/Publications/
-
- Merson M. The HIV-AIDS pandemic at 25 - the global response. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2414–2417. - PubMed
-
- Piot P, Bartos M, Ghys P, Walker N, Schwartlander B. The global impact of HIV/AIDS. Nature. 2001;410:968–973. - PubMed
-
- Flexner C. HIV drug development: the next 25 years. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:959–965. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
