GRIM-19 Expression and Function in Human Gliomas
- PMID: 20717508
- PMCID: PMC2916144
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2010.48.1.20
GRIM-19 Expression and Function in Human Gliomas
Abstract
Objective: We determined whether the expression of GRIM-19 is correlated with pathologic types and malignant grades in gliomas, and determined the function of GRIM-19 in human gliomas.
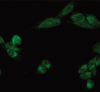
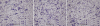
Methods: Tumor tissues were isolated and frozen at -80 just after surgery. The tissues consisted of normal brain tissue (4), astrocytomas (2), anaplastic astrocytomas (2), oligodendrogliomas (13), anaplastic oligodendrogliomas (11), and glioblastomas (16). To profile tumor-related genes, we applied RNA differential display using a Genefishing DEG kit, and validated the tumor-related genes by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). A human glioblastoma cell line (U343MG-A) was used for the GRIM-19 functional studies. The morphologic and cytoskeletal changes were examined via light and confocal microscopy. The migratory and invasive abilities were investigated by the simple scratch technique and Matrigel assay. The antiproliferative activity was determined by thiazolyl blue Tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and FACS analysis.
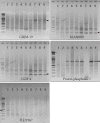
Results: Based on RT-PCR analysis, the expression of GRIM-19 was higher in astrocytic tumors than oligodendroglial tumors. The expression of GRIM-19 was higher in high-grade tumors than low-grade tumors or normal brain tissue; glioblastomas showed the highest expression. After transfection of GRIM-19 into U343MG-A, the morphology of the sense-transfection cells became larger and more spindly. The antisense-transfection cells became smaller and rounder compared with wild type U343MG-A. The MTT assay showed that the sense-transfection cells were more sensitive to the combination of interferon-beta and retinoic acid than U343MG-A cells or antisense-transfection cells; the anti-proliferative activity was related to apoptosis.
Conclusion: GRIM-19 may be one of the gene profiles which regulate cell death via apoptosis in human gliomas.
Keywords: Cell line; GRIM-19; Gene Fishing; Glioblastoma; Human glioma.
Figures





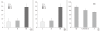

Similar articles
-
Role of galectin-1 in migration and invasion of human glioblastoma multiforme cell lines.J Neurosurg. 2008 Aug;109(2):273-84. doi: 10.3171/JNS/2008/109/8/0273. J Neurosurg. 2008. PMID: 18671640
-
Expression of interleukin-1beta mRNA and protein in human gliomas assessed by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998 Jul;57(7):653-63. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199807000-00002. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9690669
-
Expression of the oligodendroglial lineage-associated markers Olig1 and Olig2 in different types of human gliomas.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003 Oct;62(10):1052-9. doi: 10.1093/jnen/62.10.1052. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 14575240
-
Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005 Jun;64(6):479-89. doi: 10.1093/jnen/64.6.479. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15977639 Review.
-
[Histological and molecular classification of gliomas].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008 Jun-Jul;164(6-7):505-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2008.03.011. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18565348 Review. French.
Cited by
-
GRIM-19: A master regulator of cytokine induced tumor suppression, metastasis and energy metabolism.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Feb;33:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 27659873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and expression of attacin, an antibacterial protein-encoding gene, from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).Mol Biol Rep. 2012 May;39(5):5151-9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1311-3. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22160467
References
-
- Alchanati I, Nallar SC, Sun P, Gao L, Hu J, Stein A, et al. A proteomic analysis reveals the loss of expression of the cell death regulatory gene GRIM-19 in human renal cell carcinomas. Oncogene. 2006;25:7138–7147. - PubMed
-
- Angell JE, Lindner DJ, Shapiro PS, Hofmann ER, Kalvakolanu DV. Identification of GRIM-19, a novel cell death-regulatory gene induced by the interferon-beta and retinoic acid combination, using a genetic approach. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:33416–33426. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
-
- Chelbi-Alix MK, Pelicano L, Quignon F, Koken MH, Venturini L, Stadler M, et al. Induction of the PML protein by interferons in normal and APL cells. Leukemia. 1995;9:2027–2033. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

