Rapid Development of Brain Abscess Caused by Streptococcus Pyogenes Following Penetrating Skull Injury via the Ethmoidal Sinus and Lamina Cribrosa
- PMID: 20717517
- PMCID: PMC2916153
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2010.48.1.73
Rapid Development of Brain Abscess Caused by Streptococcus Pyogenes Following Penetrating Skull Injury via the Ethmoidal Sinus and Lamina Cribrosa
Abstract
Objective: Streptococcus pyogenes is a beta-hemolytic bacterium that belongs to Lancefield serogroup A, also known as group A streptococci (GAS). There have been five reported case in terms of PubMed-based search but no reported case of brain abscess caused by Streptococcus pyogenes as a result of penetrating skull injury. We present a patient who suffered from penetrating skull injury that resulted in a brain abscess caused by Streptococcus pyogenes.
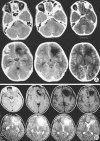
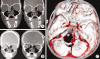
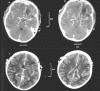
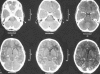
Methods: The patient was a 12-year-old boy who fell down from his bicycle while cycling and ran into a tree. A wooden stick penetrated his skin below the right lower eyelid and advanced to the cranium. He lost consciousness on the fifth day of the incident and his body temperature was measured as 40. While being admitted to our hospital, a cranial computed tomography revealed a frontal cystic mass with a perilesional hypodense zone of edema. There was no capsule formation around the lesion after intravenous contrast injection. Paranasal CT showed a bone defect located between the ethmoidal sinus and lamina cribrosa.
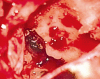
Results: Bifrontal craniotomy was performed. The abscess located at the left frontal lobe was drained and the bone defect was repaired.
Conclusion: Any penetrating lesion showing a connection between the lamina cribrosa and ethmoidal sinus may result in brain abscess caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. These patients should be treated urgently to repair the defect and drain the abscess with appropriate antibiotic therapy started due to the fulminant course of the brain abscess caused by this microorganism.
Keywords: Brain abscess; Penetrating head injury; Skull base repairing; Streptococcus pyogenes; Surgical evacuation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Brain abscess caused by Streptococcus pyogenes with atypical symptoms: a case report and literature review.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05208-w. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39528984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localized asymptomatic cerebellar abscess after penetrating brain injury by wooden foreign object with adequate antibiotics administration: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;72:85-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.05.058. Epub 2020 May 30. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32531706 Free PMC article.
-
[Delayed brain abscess after penetrating transorbital injury].No Shinkei Geka. 2007 May;35(5):481-6. No Shinkei Geka. 2007. PMID: 17491344 Japanese.
-
[Orbital cellulitis complicated by subperiosteal abscess due to Streptococcus pyogenes infection].Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2017 Mar-Apr;74(2):134-140. doi: 10.1016/j.bmhimx.2017.01.006. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2017. PMID: 29382496 Spanish.
-
Skull stab wound from a metal railroad nail perforating the right frontal lobe.Brain Inj. 2013;27(7-8):973-7. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2013.794959. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Brain Inj. 2013. PMID: 23782299 Review.
Cited by
-
Group A Streptococcal meningitis in children: a short case series and systematic review.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Aug;43(8):1517-1531. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04863-2. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38842766 Free PMC article.
-
Brain abscess caused by Streptococcus pyogenes with atypical symptoms: a case report and literature review.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05208-w. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39528984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral cavernous malformation with associated Streptococcus pyogenes abscess in a child: a case report and literature review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2024 Dec 31;41(1):76. doi: 10.1007/s00381-024-06745-6. Childs Nerv Syst. 2024. PMID: 39738866 Review.
References
-
- Aydin IH, Aladag MA, Kadioglu HH, Onder A. Clinical analysis of cerebral abscesses. Zentralbl Neurochir. 1988;49:210–219. - PubMed
-
- Bağdatoğlu H, Ildan F, Cetinalp E, Doğanay M, Boyar B, Uzuneyüpoğlu Z, et al. The clinical presentation of intracranial abscesses. A study of seventy-eight cases. J Neurosurg Sci. 1992;36:139–143. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee C, Bustamante CI, Wharton R, Talley E, Wade JC. Bacillus infections in patients with cancer. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:1769–1774. - PubMed
-
- Bard LA, Jarrett WH. Intracranial complications of penetrating orbital injuries. Arch Ophthalmol. 1964;71:332–343. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

