Urinary neopterin does not reflect the local antitumor immune milieu in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 20717669
- PMCID: PMC11030582
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0907-0
Urinary neopterin does not reflect the local antitumor immune milieu in ovarian cancer
Abstract
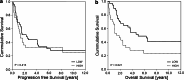
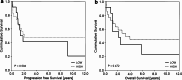
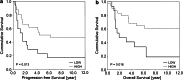
The main objective of the present investigation was to study the urinary neopterin excretion in the context of the activation of the adaptive cellular immune system at the tumor site. For this purpose, we compared pre-treatment urinary neopterin levels measured in 92 ovarian cancer patients, with intratumoral levels of mRNA transcripts from factors either involved in the adaptive antitumor immune defense (CD3, IFN-γ, IRF-1, IRF-2, SOCS1 and iNOS) or immune tolerance (FoxP3). This study did not reveal an association between urinary neopterin and one of these investigated "on tumor site transcripts". From all the factors reflecting the magnitude of the local adaptive antitumor response, intratumoral IRF-1 expression above the edge of the 25th percentile was found to predict most reliably favorable progression-free (median 34 months vs. 10 months; p < 0.001) and overall (median 52 months vs. 16 months; p < 0.001) survival. In contrast, pre-treatment urinary neopterin excretion above 275 μmol/mol creatinine, which indicates an unspecific activation of the innate immune system, was associated with a very poor overall survival with a median of only 11 months when compared with a median overall survival of 40 months in patients with lower urinary neopterin excretion (p = 0.021). Interestingly, the considerable survival benefit in patients with high IRF-1-expressing cancers was completely abrogated as well for progression-free as for overall survival when urinary neopterin concentrations were found to be concomitantly elevated. These findings demonstrate that in ovarian carcinomas the unspecific "cancer-related inflammation" contributes to a significant subversion of the adaptive antitumor immune defense mounted at the tumor site.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-term significance of urinary neopterin in ovarian cancer: a study by the Austrian Association for Gynecologic Oncology (AGO).Ann Oncol. 2016 Sep;27(9):1740-6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw248. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27358381
-
The expression of the regulatory T cell-specific forkhead box transcription factor FoxP3 is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 1;11(23):8326-31. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1244. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16322292
-
[Activation of the immune system in colorectal carcinoma and its assessment].Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) Suppl. 1997;40(2):81-2. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) Suppl. 1997. PMID: 10103145 Czech.
-
Neopterin as an indicator of immune activation and prognosis in patients with gynecological malignancies.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006 Jan-Feb;16(1):240-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00294.x. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16445639 Review.
-
Cellular immune activation, neopterin production, tryptophan degradation and the development of immunodeficiency.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000;48(4):251-8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000. PMID: 11059641 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary neopterin levels in patients with thyroid cancer.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Sep;66(3):302-8. doi: 10.1007/s12070-014-0710-x. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014. PMID: 25032119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakurei A, Goto M. Neopterin: isolation from human urine. J Biochem. 1967;61:142–145. - PubMed
-
- Huber C, Batchelor JR, Fuchs D, Hausen A, Lang A, Niederwieser D, Reibnegger G, Swetly P, Troppmair J, Wachter H. Immune response associated production of neopterin. Release from macrophages primarily under the control of interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1984;160:310–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.310. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hofmann B, Bass H, Nishanian P, Faisal M, Figlin RA, Sarna GP, Fahey JL. Different lymphoid cell populations produce varied levels of neopterin, beta 2-microglobulin and soluble IL-2 receptor when stimulated with IL-2, interferon-gamma or tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992;88:548–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06485.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

