Pancreatic cyst fluid and serum mucin levels predict dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas
- PMID: 20717734
- PMCID: PMC4241376
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-010-1225-7
Pancreatic cyst fluid and serum mucin levels predict dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas
Abstract
Introduction: There are no reliable markers of dysplasia in patients with incidentally discovered intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas (IPMN). IPMN dysplasia may be associated with mucin protein (MUC) expression and histopathologic subtype. We hypothesize that MUC expression in cyst fluid and serum can identify lesions with high risk of malignancy.
Methods: Cyst fluid and serum were collected from 40 patients during pancreatectomy for IPMN between 2005 and 2009. Samples were grouped into low-risk (low-grade or moderate dysplasia, n = 21) and high-risk groups (high-grade dysplasia or carcinoma, n = 19). Mucin expression (MUC1, MUC2, MUC4, and MUC5AC) was assessed utilizing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
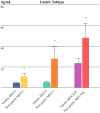
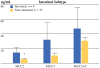
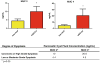
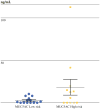
Results: MUC2 and MUC4 cyst fluid concentrations were elevated in high-risk versus low-risk groups (10 ± 3.0 ng/ml vs. 4.4 ± 1.2 ng/ml, p = 0.03; 20.6 ± 10.6 ng/ml vs. 4.5 ± 1.4 ng/ml, p = 0.03, respectively). Corresponding serum samples revealed higher levels of MUC5AC in high-risk compared with low-risk patients (19.9 ± 9.3 ng/ml vs. 2.2 ± 1.1 ng/ml, p = 0.04). Histopathologic subtype was significantly associated with grade of dysplasia, and the intestinal subtype displayed increased MUC2 cyst fluid concentrations (13.8 ± 6.5 ng/ml vs. 4.1 ± 0.9 ng/ml, p = 0.02).
Conclusions: In this study, high-risk IPMN showed elevated cyst fluid concentrations of MUC2 and MUC4, and increased serum levels of MUC5AC. High-risk IPMN also displayed a distinct mucin expression profile in specific histologic subtypes. These data, if validated, may allow surgeons to more appropriately select patients for operative resection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mucin gene expression in intraductal papillary-mucinous pancreatic tumours and related lesions.J Pathol. 2002 Aug;197(5):632-7. doi: 10.1002/path.1146. J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12210083
-
[Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of pancreas].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Feb;35(2):77-81. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16630480 Chinese.
-
Pancreatic Fluid Interleukin-1β Complements Prostaglandin E2 and Serum Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 in Prediction of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Dysplasia.Pancreas. 2019 Sep;48(8):1026-1031. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001377. Pancreas. 2019. PMID: 31404023 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty years of experience with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: from discovery to international consensus.Digestion. 2014;90(4):265-72. doi: 10.1159/000370111. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Digestion. 2014. PMID: 25591885 Review.
-
[Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas, IPMN].Duodecim. 2013;129(6):591-8. Duodecim. 2013. PMID: 23614224 Review. Finnish.
Cited by
-
Tumor-associated Neutrophils and Malignant Progression in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms: An Opportunity for Identification of High-risk Disease.Ann Surg. 2015 Dec;262(6):1102-7. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001044. Ann Surg. 2015. PMID: 25563865 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnosis and management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: has progress been made?Updates Surg. 2019 Jun;71(2):209-216. doi: 10.1007/s13304-019-00661-0. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Updates Surg. 2019. PMID: 31175628 Review.
-
Molecular Pathology of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions with a Focus on Malignant Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;16(6):1183. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061183. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucin Expression in Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts: Can String Sign Test Predict Mucin Types? A Single Center Pilot Study.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb;32(2):187-193. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2020.20060. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33960943 Free PMC article.
-
The use of protein-based biomarkers for the diagnosis of cystic tumors of the pancreas.Int J Proteomics. 2011;2011:413646. doi: 10.1155/2011/413646. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Int J Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 22110950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang XM, Mitchell DG, Dohke M, Holland GA, Parker L. Pancreatic cysts: Depiction on single-shot fast spin-echo MR images. Radiology. 2002;223:547–53. - PubMed
-
- Maker AV, Lee LS, Raut CP, Clancy TE, Swanson RS. Cytology from pancreatic cysts has marginal utility in surgical decision-making. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:3187–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

