A cell-based screen for inhibitors of protein folding and degradation
- PMID: 20717760
- PMCID: PMC3024082
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-010-0200-3
A cell-based screen for inhibitors of protein folding and degradation
Abstract
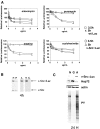
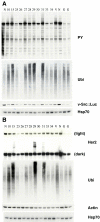
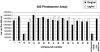
Cancer cells are exposed to external and internal stresses by virtue of their unrestrained growth, hostile microenvironment, and increased mutation rate. These stresses impose a burden on protein folding and degradation pathways and suggest a route for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Proteasome and Hsp90 inhibitors are in clinical trials and a 20S proteasome inhibitor, Velcade, is an approved drug. Other points of intervention in the folding and degradation pathway may therefore be of interest. We describe a simple screen for inhibitors of protein synthesis, folding, and proteasomal degradation pathways in this paper. The molecular chaperone-dependent client v-Src was fused to firefly luciferase and expressed in HCT-116 colorectal tumor cells. Both luciferase and protein tyrosine kinase activity were preserved in cells expressing this fusion construct. Exposing these cells to the Hsp90 inhibitor geldanamycin caused a rapid reduction of luciferase and kinase activities and depletion of detergent-soluble v-Src::luciferase fusion protein. Hsp70 knockdown reduced v-Src::luciferase activity and, when combined with geldanamycin, caused a buildup of v-Src::luciferase and ubiquitinated proteins in a detergent-insoluble fraction. Proteasome inhibitors also decreased luciferase activity and caused a buildup of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in a detergent-insoluble fraction. Protein synthesis inhibitors also reduced luciferase activity, but had less of an effect on phosphotyrosine levels. In contrast, certain histone deacetylase inhibitors increased luciferase and phosphotyrosine activity. A mass screen led to the identification of Hsp90 inhibitors, ubiquitin pathway inhibitors, inhibitors of Hsp70/Hsp40-mediated refolding, and protein synthesis inhibitors. The largest group of compounds identified in the screen increased luciferase activity, and some of these increase v-Src levels and activity. When used in conjunction with appropriate secondary assays, this screen is a powerful cell-based tool for studying compounds that affect protein synthesis, folding, and degradation.
Figures










Similar articles
-
The heat shock protein 90 antagonist geldanamycin alters chaperone association with p210bcr-abl and v-src proteins before their degradation by the proteasome.Cell Growth Differ. 2000 Jul;11(7):355-60. Cell Growth Differ. 2000. PMID: 10939589
-
Endoplasmic reticulum vacuolization and valosin-containing protein relocalization result from simultaneous hsp90 inhibition by geldanamycin and proteasome inhibition by velcade.Mol Cancer Res. 2006 Sep;4(9):667-81. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0019. Mol Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16966435
-
Simultaneous inhibition of hsp 90 and the proteasome promotes protein ubiquitination, causes endoplasmic reticulum-derived cytosolic vacuolization, and enhances antitumor activity.Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 May;3(5):551-66. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004. PMID: 15141013
-
The Hsp70-Hsp90 go-between Hop/Stip1/Sti1 is a proteostatic switch and may be a drug target in cancer and neurodegeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(23):7257-7273. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03962-z. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34677645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic Small Molecule Modulators of Hsp70 and Hsp40 Chaperones as Promising Anticancer Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 17;24(4):4083. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044083. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic stress controls mutant p53 R248Q stability in acute myeloid leukemia cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 4;9(1):5637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42220-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30948782 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting novel structural and functional features of coronavirus protease nsp5 (3CLpro, Mpro) in the age of COVID-19.J Gen Virol. 2021 Mar;102(3):001558. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001558. Epub 2021 Jan 28. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 33507143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S, Elliott PJ. Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2615–2622. - PubMed
-
- An WG, Schulte TW, Neckers LM. The heat shock protein 90 antagonist geldanamycin alters chaperone association with p210bcr-abl and v-src proteins before their degradation by the proteasome. Cell Growth Differ. 2000;11:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, Rocha K, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S, Atadja P, Seto E, Bhalla K. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26729–26734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500186200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brough PA, Aherne W, Barril X, Borgognoni J, Boxall K, Cansfield JE, Cheung KM, Collins I, Davies NG, Drysdale MJ, Dymock B, Eccles SA, Finch H, Fink A, Hayes A, Howes R, Hubbard RE, James K, Jordan AM, Lockie A, Martins V, Massey A, Matthews TP, McDonald E, Northfield CJ, Pearl LH, Prodromou C, Ray S, Raynaud FI, Roughley SD, Sharp SY, Surgenor A, Walmsley DL, Webb P, Wood M, Workman P, Wright L. 4,5-Diarylisoxazole Hsp90 chaperone inhibitors: potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. 2008;51:196–218. doi: 10.1021/jm701018h. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

