Emodin, a natural product, selectively inhibits 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and ameliorates metabolic disorder in diet-induced obese mice
- PMID: 20718744
- PMCID: PMC2962821
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00826.x
Emodin, a natural product, selectively inhibits 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and ameliorates metabolic disorder in diet-induced obese mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11beta-HSD1) is an attractive therapeutic target of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Emodin, a natural product and active ingredient of various Chinese herbs, has been demonstrated to possess multiple biological activities. Here, we investigated the effects of emodin on 11beta-HSD1 and its ability to ameliorate metabolic disorders in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice.
Experimental approach: Scintillation proximity assay was performed to evaluate inhibition of emodin against recombinant human and mouse 11beta-HSDs. The ability of emodin to inhibit prednisone- or dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance was investigated in C57BL/6J mice and its effect on metabolic abnormalities was observed in DIO mice.
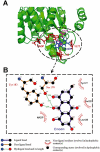
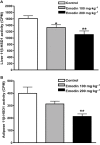
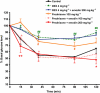
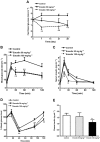
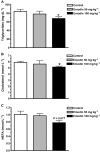
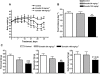
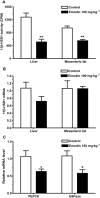
Key results: Emodin is a potent and selective 11beta-HSD1 inhibitor with the IC(50) of 186 and 86 nM for human and mouse 11beta-HSD1, respectively. Single oral administration of emodin inhibited 11beta-HSD1 activity of liver and fat significantly in mice. Emodin reversed prednisone-induced insulin resistance in mice, whereas it did not affect dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance, which confirmed its inhibitory effect on 11beta-HSD1 in vivo. In DIO mice, oral administration of emodin improved insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism, and lowered blood glucose and hepatic PEPCK, and glucose-6-phosphatase mRNA.
Conclusions and implications: This study demonstrated a new role for emodin as a potent and selective inhibitor of 11beta-HSD1 and its beneficial effects on metabolic disorders in DIO mice. This highlights the potential value of analogues of emodin as a new class of compounds for the treatment of metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emodin, an 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, regulates adipocyte function in vitro and exerts anti-diabetic effect in ob/ob mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Sep;33(9):1195-203. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.87. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22922341 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effect of a novel selective 11β-HSD1 inhibitor in the diet-induced obese mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.052. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24135201
-
Anti-diabetic and anti-adipogenic effects of a novel selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor in the diet-induced obese mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 15;691(1-3):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.06.024. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22760069
-
Tissue-specific glucocorticoid reactivating enzyme, 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11 beta-HSD1)--a promising drug target for the treatment of metabolic syndrome.Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2003 Dec;3(4):255-62. doi: 10.2174/1568008033340135. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2003. PMID: 14683456 Review.
-
11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and obesity.Front Horm Res. 2008;36:146-164. doi: 10.1159/000115363. Front Horm Res. 2008. PMID: 18230901 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of Anthraquinone-2-Carboxylic Acid.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:1903849. doi: 10.1155/2016/1903849. Epub 2016 Jan 3. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27057092 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin, an 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, regulates adipocyte function in vitro and exerts anti-diabetic effect in ob/ob mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Sep;33(9):1195-203. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.87. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22922341 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin regulating excision repair cross-complementation group 1 through fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Apr 28;19(16):2481-91. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i16.2481. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23674849 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between GSK-3β-actuated molecular cascades and myocardial physiology.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Nov;26(6):1495-1504. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-09961-9. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 32314086 Review.
-
Emodin and rhein decrease levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human pancreatic cancer cells and attenuate cancer cachexia in athymic mice carrying these cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 27;8(50):88008-88020. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21330. eCollection 2017 Oct 20. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29152137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdallah BM, Beck-Nielsen H, Gaster M. Increased expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in type 2 diabetic myotubes. Eur J Clin Invest. 2005;35:627–634. - PubMed
-
- Alberts P, Nilsson C, Selen G, Engblom LO, Edling NH, Norling S, et al. Selective inhibition of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in hyperglycemic mice strains. Endocrinology. 2003;144:4755–4762. - PubMed
-
- Andrews RC, Rooyackers O, Walker BR. Effects of the 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitor carbenoxolone on insulin sensitivity in men with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Beauregard C, Dickstein G, Lacroix A. Classic and recent etiologies of Cushing's syndrome: diagnosis and therapy. Treat Endocrinol. 2002;1:79–94. - PubMed
-
- Cavagnini F, Croci M, Putignano P, Petroni ML, Invitti C. Glucocorticoids and neuroendocrine function. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24:S77–S79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

