Robust anti-arrhythmic efficacy of verapamil and flunarizine against dofetilide-induced TdP arrhythmias is based upon a shared and a different mode of action
- PMID: 20718748
- PMCID: PMC2962825
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00883.x
Robust anti-arrhythmic efficacy of verapamil and flunarizine against dofetilide-induced TdP arrhythmias is based upon a shared and a different mode of action
Abstract
Background and purpose: The high predisposition to Torsade de Pointes (TdP) in dogs with chronic AV-block (CAVB) is well documented. The anti-arrhythmic efficacy and mode of action of Ca(2+) channel antagonists, flunarizine and verapamil against TdP were investigated.
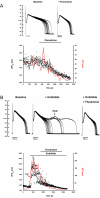
Experimental approach: Mongrel dogs with CAVB were selected based on the inducibility of TdP with dofetilide. The effects of flunarizine and verapamil were assessed after TdP and in different experiments to prevent dofetilide-induced TdP. Electrocardiogram and ventricular monophasic action potentials were recorded. Electrophysiological parameters and short-term variability of repolarization (STV) were determined. In vitro, flunarizine and verapamil were added to determine their effect on (i) dofetilide-induced early after depolarizations (EADs) in canine ventricular myocytes (VM); (ii) diastolic Ca(2+) sparks in RyR2(R4496+/+) mouse myocytes; and (iii) peak and late I(Na) in SCN5A-HEK 293 cells.
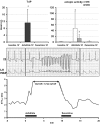
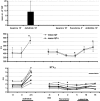
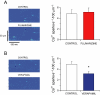
Key results: Dofetilide increased STV prior to TdP and in VM prior to EADs. Both flunarizine and verapamil completely suppressed TdP and reversed STV to baseline values. Complete prevention of TdP was achieved with both drugs, accompanied by the prevention of an increase in STV. Suppression of EADs was confirmed after flunarizine. Only flunarizine blocked late I(Na). Ca(2+) sparks were reduced with verapamil.
Conclusions and implications: Robust anti-arrhythmic efficacy was seen with both Ca(2+) channel antagonists. Their divergent electrophysiological actions may be related to different additional effects of the two drugs.
Figures
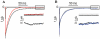
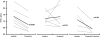
References
-
- Aiba T, Shimizu W, Inagaki M, Noda T, Miyoshi S, Ding WG, et al. Cellular and ionic mechanism for drug-induced long QT syndrome and effectiveness of verapamil. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:300–307. - PubMed
-
- Anderson ME, Braun AP, Wu Y, Lu T, Wu Y, Schulman H, et al. KN-93, an inhibitor of multifunctional Ca++/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, decreases early afterdepolarizations in rabbit heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;287:996–1006. - PubMed
-
- Antoons G, Oros A, Beekman JDM, Engelen MA, Houtman MJ, Belardinelli L, et al. Late Na+ current inhibition by Ranolazine reduces Torsades de Pointes in the chronic atrioventricular block dog model. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:801–809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

