Exogenous introduction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 reduces accelerated growth of TGF-β-disrupted diffuse-type gastric carcinoma
- PMID: 20718757
- PMCID: PMC11159670
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01688.x
Exogenous introduction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 reduces accelerated growth of TGF-β-disrupted diffuse-type gastric carcinoma
Abstract
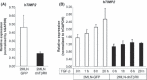
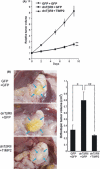
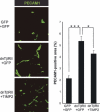
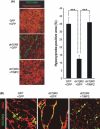
Diffuse-type gastric carcinoma is characterized by rapid progression and poor prognosis. High expression of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and thick stromal fibrosis are observed in this type of gastric carcinoma. We have previously shown that disruption of TGF-β signaling via introduction of a dominant negative form of the TGF-β type II receptor (dnTβRII) into diffuse-type gastric cancer cell lines, including OCUM-2MLN, caused accelerated tumor growth through induction of tumor angiogenesis in vivo. In the present study, we show that TGF-β induces upregulation of expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP2) in the OCUM-2MLN cell line in vitro, and that expression of TIMP2 is repressed by dnTβRII expression in vivo. Transplantation of the OCUM-2MLN cells to nude mice exhibited accelerated tumor growth in response to dnTβRII expression, which was completely abolished when TIMP2 was coexpressed with dnTβRII. Although the blood vessel density of TIMP2-expressing tumors was only slightly decreased, the degree of hypoxia in tumor tissues was significantly increased and pericytes covering tumor vasculature were decreased by TIMP2 expression in OCUM-2MLN cells, suggesting that the function of tumor vasculatures was repressed by TIMP2 and consequently tumor growth was reduced. These findings provide evidence that one of the mechanisms of the increase in angiogenesis in diffuse-type gastric carcinoma is the downregulation of the anti-angiogenic protein TIMP2.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diffuse-type gastric carcinoma: progression, angiogenesis, and transforming growth factor beta signaling.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 Apr 15;101(8):592-604. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp058. Epub 2009 Apr 7. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009. PMID: 19351925 Free PMC article.
-
c-Ski overexpression promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis through inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in diffuse-type gastric carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2009 Oct;100(10):1809-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01248.x. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19594546 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β suppresses metastasis in a subset of human colon carcinoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2012 Jun 6;12:221. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-221. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22672900 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated expression of REG4 and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 regulating tumourigenic capacity of diffuse-type gastric carcinoma-initiating cells is inhibited by TGF-β.J Pathol. 2012 Nov;228(3):391-404. doi: 10.1002/path.4020. Epub 2012 May 8. J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22430847
-
TGF-betas and TGF-beta receptors in atherosclerosis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Mar-Jun;11(1-2):103-14. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00034-9. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10708958 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer stem cells: the 'heartbeat' of gastric cancer.J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul;48(7):781-97. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0712-y. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23184096 Review.
-
MiR-301a promotes cell proliferation by directly targeting TIMP2 in multiple myeloma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Aug 1;8(8):9168-74. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26464662 Free PMC article.
-
αvβ6 integrin is required for TGFβ1-mediated matrix metalloproteinase2 expression.Biochem J. 2015 Mar 15;466(3):525-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140698. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25558779 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 play tumor suppressive roles in human diffuse-type gastric carcinoma.Am J Pathol. 2011 Dec;179(6):2920-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.08.022. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21996676 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis Identifies a Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Signature for Predicting Prognosis and Therapeutic Responses in Gastric Cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Oct 8;8:744677. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.744677. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34692770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brenner H, Rothenbacher D, Arndt V. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol 2009; 472: 467–77. - PubMed
-
- Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so‐called intestinal‐type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo‐clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 1965; 64: 31–49. - PubMed
-
- Mizoi T, Ohtani H, Miyazono K, Miyazawa M, Matsuno S, Nagura H. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of transforming growth factor beta 1 and latent transforming growth factor beta 1 binding protein in human gastrointestinal carcinomas: qualitative difference between cancer cells and stromal cells. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 183–90. - PubMed
-
- Kinugasa S, Abe S, Tachibana M et al. Overexpression of transforming growth factor‐beta1 in scirrhous carcinoma of the stomach correlates with decreased survival. Oncology 1998; 55: 582–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

