Inhibition of allogeneic inflammatory responses by the Ribonucleotide Reductase Inhibitors, Didox and Trimidox
- PMID: 20718971
- PMCID: PMC2933664
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-43
Inhibition of allogeneic inflammatory responses by the Ribonucleotide Reductase Inhibitors, Didox and Trimidox
Abstract
Background: Graft-versus-host disease is the single most important obstacle facing successful allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT). Even with current immunosuppressive therapies, morbidity and mortality rates are high. Current therapies including cyclosporine A (CyA) and related compounds target IL-2 signaling. However, although these compounds offer great benefit, they are also associated with multiple toxicities. Therefore, new compounds with a greater efficacy and reduced toxicity are needed to enable us to overcome this hurdle.
Methods: The allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) is a unique ex vivo method to study a drug's action on the initial events resulting in T-cell activation and proliferation, synonymous to the initial stages of tissue and organ destruction by T-cell responses in organ rejection and Graft-versus-host disease. Using this approach, we examined the effectiveness of two ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors (RRI), Didox and Trimidox, to inhibit T-cell activation and proliferation.
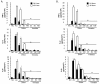
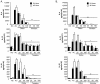
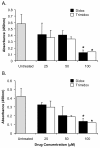
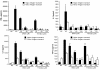
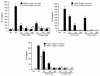
Results: The compounds caused a marked reduction in the proliferative responses of T-cells, which is also accompanied by decreased secretion of cytokines IL-6, IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, IL-2, IL-13, IL-10 and IL-4.
Conclusions: In conclusion, these data provide critical information to justify further investigation into the potential use of these compounds post allogeneic bone marrow transplantation to alleviate graft-versus-host disease thereby achieving better outcomes.
Figures
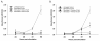
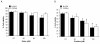
References
-
- Hong JC, Kahan BD. Immunosuppressive agents in organ transplantation: past, present, and future. Seminars in nephrology. 2000;20:108–25. - PubMed
-
- Yarbro JW. Mechanism of action of hydroxyurea. Seminars in oncology. 1992;19:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy BJ. The evolution of hydroxyurea therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Seminars in oncology. 1992;19:21–6. - PubMed
-
- Kiladjian JJ, Rain JD, Bernard JF, Briere J, Chomienne C, Fenaux P. Long-term incidence of hematological evolution in three French prospective studies of hydroxyurea and pipobroman in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Seminars in thrombosis and hemostasis. 2006;32:417–21. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-942762. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

