Chk1-dependent constitutive phosphorylation of BLM helicase at serine 646 decreases after DNA damage
- PMID: 20719863
- PMCID: PMC2941563
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0233
Chk1-dependent constitutive phosphorylation of BLM helicase at serine 646 decreases after DNA damage
Abstract
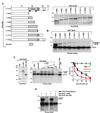
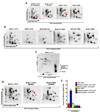
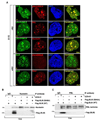
BLM helicase, the protein mutated in Bloom syndrome, is involved in signal transduction cascades after DNA damage. BLM is phosphorylated on multiple residues by different kinases either after stress induction or during mitosis. Here, we have provided evidence that both Chk1 and Chk2 phosphorylated the NH(2)-terminal 660 amino acids of BLM. An internal region within the DExH motif of BLM negatively regulated the Chk1/Chk2-dependent NH(2)-terminal phosphorylation event. Using in silico analysis involving the Chk1 structure and its known substrate specificity, we predicted that Chk1 should preferentially phosphorylate BLM on serine 646 (Ser(646)). The prediction was validated in vitro by phosphopeptide analysis on BLM mutants and in vivo by usage of a newly generated phosphospecific polyclonal antibody. We showed that the phosphorylation at Ser(646) on BLM was constitutive and decreased rapidly after exposure to DNA damage. This resulted in the diminished interaction of BLM with nucleolin and PML isoforms, and consequently decreased BLM accumulation in the nucleolus and PML nuclear bodies. Instead, BLM relocalized to the sites of DNA damage and bound with the damage sensor protein, Nbs1. Mutant analysis confirmed that the binding to nucleolin and PML isoforms required Ser(646) phosphorylation. These results indicated that Chk1-mediated phosphorylation on BLM at Ser(646) might be a determinant for regulating subnuclear localization and could act as a marker for the activation status of BLM in response to DNA damage.
© 2010 AACR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chk1 protects against chromatin bridges by constitutively phosphorylating BLM serine 502 to inhibit BLM degradation.J Cell Sci. 2014 Sep 15;127(Pt 18):3902-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.155176. Epub 2014 Jul 11. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25015292
-
p53 C-terminal phosphorylation by CHK1 and CHK2 participates in the regulation of DNA-damage-induced C-terminal acetylation.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Apr;16(4):1684-95. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0689. Epub 2005 Jan 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15659650 Free PMC article.
-
The Bloom syndrome helicase is a substrate of the mitotic Cdc2 kinase.Cell Cycle. 2006 Aug;5(15):1681-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.15.3122. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16880735
-
Kinases that control the cell cycle in response to DNA damage: Chk1, Chk2, and MK2.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;21(2):245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.01.018. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19230643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features of Bloom syndrome and function of the causative gene, BLM helicase.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2004 May;4(3):393-401. doi: 10.1586/14737159.4.3.393. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2004. PMID: 15137905 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of BLM Nucleolar Localization.Genes (Basel). 2016 Sep 21;7(9):69. doi: 10.3390/genes7090069. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27657136 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated BLM peptide acts as an agonist for DNA damage response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkaf106. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf106. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39997217 Free PMC article.
-
A Network of Conserved Synthetic Lethal Interactions for Exploration of Precision Cancer Therapy.Mol Cell. 2016 Aug 4;63(3):514-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.022. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27453043 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Chk1 in cell biology and cancer therapy.Int J Cancer. 2014 Mar 1;134(5):1013-23. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28226. Epub 2013 May 28. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23613359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemogenetic profiling identifies RAD17 as synthetically lethal with checkpoint kinase inhibition.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 3;6(34):35755-69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5928. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26437225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hurley PJ, Bunz F. ATM and ATR: components of an integrated circuit. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Bartek J, Lukas J. Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:421–429. - PubMed
-
- Hickson ID. RecQ helicases: caretakers of the genome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:169–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

