Subribosomal particle analysis reveals the stages of bacterial ribosome assembly at which rRNA nucleotides are modified
- PMID: 20719918
- PMCID: PMC2941110
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2160010
Subribosomal particle analysis reveals the stages of bacterial ribosome assembly at which rRNA nucleotides are modified
Abstract
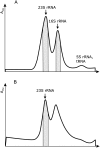
Modified nucleosides of ribosomal RNA are synthesized during ribosome assembly. In bacteria, each modification is made by a specialized enzyme. In vitro studies have shown that some enzymes need the presence of ribosomal proteins while other enzymes can modify only protein-free rRNA. We have analyzed the addition of modified nucleosides to rRNA during ribosome assembly. Accumulation of incompletely assembled ribosomal particles (25S, 35S, and 45S) was induced by chloramphenicol or erythromycin in an exponentially growing Escherichia coli culture. Incompletely assembled ribosomal particles were isolated from drug-treated and free 30S and 50S subunits and mature 70S ribosomes from untreated cells. Nucleosides of 16S and 23S rRNA were prepared and analyzed by reverse-phase, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Pseudouridines were identified by the chemical modification/primer extension method. Based on the results, the rRNA modifications were divided into three major groups: early, intermediate, and late assembly specific modifications. Seven out of 11 modified nucleosides of 16S rRNA were late assembly specific. In contrast, 16 out of 25 modified nucleosides of 23S rRNA were made during early steps of ribosome assembly. Free subunits of exponentially growing bacteria contain undermodified rRNA, indicating that a specific set of modifications is synthesized during very late steps of ribosome subunit assembly.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Random pseuoduridylation in vivo reveals critical region of Escherichia coli 23S rRNA for ribosome assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):6098-6108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx160. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28334881 Free PMC article.
-
Crosslinking of 4.5S RNA to the Escherichia coli ribosome in the presence or absence of the protein Ffh.RNA. 2002 May;8(5):612-25. doi: 10.1017/s1355838202020095. RNA. 2002. PMID: 12022228 Free PMC article.
-
Role of pseudouridine in structural rearrangements of helix 69 during bacterial ribosome assembly.ACS Chem Biol. 2012 May 18;7(5):871-8. doi: 10.1021/cb200497q. Epub 2012 Feb 24. ACS Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22324880 Free PMC article.
-
What do we know about ribosomal RNA methylation in Escherichia coli?Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25511423 Review.
-
RNA-protein interactions in the Escherichia coli ribosome.Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):927-36. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90134-m. Biochimie. 1991. PMID: 1720671 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering a delicate balance between endonuclease RNase III and ribosomal protein S15 in E. coli ribosome assembly.Biochimie. 2021 Dec;191:104-117. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 34508826 Free PMC article.
-
16S rRNA methyltransferase KsgA contributes to oxidative stress and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 3;14(1):26484. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78296-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39489773 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Post-Transcriptional Modifications in Two Large Subunit Intermediates Populated in E. coli Cells Expressing Helicase Inactive R331A DbpA.Biochemistry. 2022 May 17;61(10):833-842. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00096. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35481783 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity and conditional essentiality of modification enzymes for domain V of Escherichia coli 23S ribosomal RNA.RNA. 2022 Jun;28(6):796-807. doi: 10.1261/rna.079096.121. Epub 2022 Mar 8. RNA. 2022. PMID: 35260421 Free PMC article.
-
RlmQ: a newly discovered rRNA modification enzyme bridging RNA modification and virulence traits in Staphylococcus aureus.RNA. 2024 Feb 16;30(3):200-212. doi: 10.1261/rna.079850.123. RNA. 2024. PMID: 38164596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adesnik M, Levinthal C 1969. Synthesis and maturation of ribosomal RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 46: 281–303 - PubMed
-
- Al Refaii A, Alix J 2009. Ribosome biogenesis is temperature-dependent and delayed in Escherichia coli lacking the chaperones DnaK or DnaJ. Mol Microbiol 71: 748–762 - PubMed
-
- Andersen N, Douthwaite S 2006. YebU is a m5C methyltransferase specific for 16 S rRNA nucleotide 1407. J Mol Biol 359: 777–786 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
