Hypertension induced by angiotensin II and a high salt diet involves reduced SK current and increased excitability of RVLM projecting PVN neurons
- PMID: 20719931
- PMCID: PMC2997020
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01013.2009
Hypertension induced by angiotensin II and a high salt diet involves reduced SK current and increased excitability of RVLM projecting PVN neurons
Erratum in
- J Neurophysiol. 2011 Feb;105(2):987
Abstract
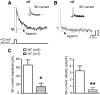
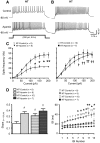
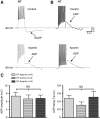
Although evidence indicates that activation of presympathetic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) neurons contributes to the pathogenesis of salt-sensitive hypertension, the underlying cellular mechanisms are not fully understood. Recent evidence indicates that small conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (SK) channels play a significant role in regulating the excitability of a key group of sympathetic regulatory PVN neurons, those with axonal projections to the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM; i.e., PVN-RVLM neurons). In the present study, rats consuming a high salt (2% NaCl) diet were made hypertensive by systemic infusion of angiotensin II (AngII), and whole cell patch-clamp recordings were made in brain slice from retrogradely labeled PVN-RVLM neurons. To determine if the amplitude of SK current was altered in neurons from hypertensive rats, voltage-clamp recordings were performed to isolate SK current. Results indicate that SK current amplitude (P < 0.05) and density (P < 0.01) were significantly smaller in the hypertensive group. To investigate the impact of this on intrinsic excitability, current-clamp recordings were performed in separate groups of PVN-RVLM neurons. Results indicate that the frequency of spikes evoked by current injection was significantly higher in the hypertensive group (P < 0.05-0.01). Whereas bath application of the SK channel blocker apamin significantly increased discharge of neurons from normotensive rats (P < 0.05-0.01), no effect was observed in the hypertensive group. In response to ramp current injections, subthreshold depolarizing input resistance was greater in the hypertensive group compared with the normotensive group (P < 0.05). Blockade of SK channels increased depolarizing input resistance in normotensive controls (P < 0.05) but had no effect in the hypertensive group. On termination of current pulses, a medium afterhyperpolarization potential (mAHP) was observed in most neurons of the normotensive group. In the hypertensive group, the mAHP was either small or absent. In the latter case, an afterdepolarization potential (ADP) was observed that was unaffected by apamin. Apamin treatment in the normotensive group blocked the mAHP and revealed an ADP resembling that seen in the hypertensive group. We conclude that diminished SK current likely underlies the absence of mAHPs in PVN-RVLM neurons from hypertensive rats. Both the ADP and greater depolarizing input resistance likely contribute to increased excitability of PVN-RVLM neurons from rats with AngII-Salt hypertension.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sympathoexcitation in ANG II-salt hypertension involves reduced SK channel function in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;308(12):H1547-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00832.2014. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25862832 Free PMC article.
-
Excitability of paraventricular nucleus neurones that project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla is regulated by small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels.J Physiol. 2009 Sep 1;587(Pt 17):4235-47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.175364. Epub 2009 Jul 6. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19581379 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term High Salt Intake Involves Reduced SK Currents and Increased Excitability of PVN Neurons with Projections to the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla in Rats.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:7282834. doi: 10.1155/2017/7282834. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 29362678 Free PMC article.
-
Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels as targets of CNS drug development.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Jun;3(3):161-7. doi: 10.2174/1568007043337472. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15180477 Review.
-
Regulation of sympathetic vasomotor activity by the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in normotensive and hypertensive states.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):H1200-H1214. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00216.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30095973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional coupling between NMDA receptors and SK channels in rat hypothalamic magnocellular neurons: altered mechanisms during heart failure.J Physiol. 2021 Jan;599(2):507-520. doi: 10.1113/JP278910. Epub 2019 Dec 4. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 31667845 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide inhibits neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus via potassium channel activation.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019 Jul 1;317(1):R121-R133. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00054.2019. Epub 2019 May 1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31042419 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic Ion Channels in Hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018 Feb 26;20(2):14. doi: 10.1007/s11906-018-0814-x. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018. PMID: 29480403 Review.
-
Interleukin-10 inhibits angiotensin II-induced decrease in neuronal potassium current.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Apr 15;304(8):C801-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00398.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23426971 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathoexcitation in ANG II-salt hypertension involves reduced SK channel function in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;308(12):H1547-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00832.2014. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25862832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barth SW, Gerstberger R. Differential regulation of angiotensinogen and AT1A receptor mRNA within the rat subfornical organ during dehydration. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 64: 151–164, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Biancardi VC, Campos RR, Stern JE. Altered balance of gamma-aminobutyric acidergic and glutamatergic afferent inputs in rostral ventrolateral medulla-projecting neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of renovascular hypertensive rats. J Comp Neurol 518: 567–585, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bond CT, Maylie J, Adelman JP. SK channels in excitability, pacemaking and synaptic integration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15: 305–311, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Brenner R, Chen QH, Vilaythong A, Toney GM, Noebels JL, Aldrich RW. BK channel beta4 subunit reduces dentate gyrus excitability and protects against temporal lobe seizures. Nat Neurosci 8: 1752–1759, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

