Modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450s by Citrobacter rodentium infection in interleukin-6- and interferon-{gamma}-null mice
- PMID: 20719939
- PMCID: PMC3202470
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.110.171488
Modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450s by Citrobacter rodentium infection in interleukin-6- and interferon-{gamma}-null mice
Abstract
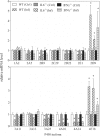
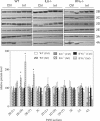
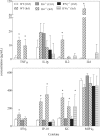
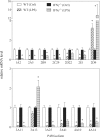
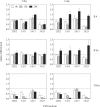
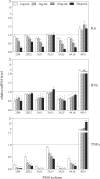
After infection with Citrobacter rodentium, murine hepatic cytochrome P450 (P450) mRNAs are selectively regulated. Several serum proinflammatory cytokines are elevated, the most abundant being interleukin-6 (IL6). To elucidate the role of cytokines in the regulation of P450s during infection, we orally infected wild-type, IL6(-/-), or interferon-γ(-/-) [IFNγ(-/-)] female C57BL/6J mice with C. rodentium and analyzed hepatic P450 expression 7 days later. The majority of P450 mRNAs were equally affected by infection in each genotype, indicating that IL6 and IFNγ are not the primary mediators of P450 down-regulation in this disease model. The down-regulation of CYP3A11 and CYP3A13 and induction of CYP2D9 mRNAs were attenuated in the IL6(-/-) mice, suggesting a role of IL6 in the regulation of only these P450s. Similar evidence implicated IFNγ in the regulation of CYP2D9, CYP2D22, CYP3A11, CYP3A25, and CYP4F18 mRNAs in C. rodentium infection and CYP2B9, CYP2D22, and CYP2E1 in the bacterial lipopolysaccharide model of inflammation. This is the first indication of an in vivo role for IFNγ in hepatic P450 regulation in disease states. The deficiency of IL6 or IFNγ affected serum levels of the other cytokines. Moreover, experiments in cultured hepatocytes demonstrated that tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) is the most potent and efficacious of the cytokines tested in the regulation of murine P450 expression. It is therefore possible that part of the IFNγ(-/-) and IL6(-/-) phenotypes could be attributed to the reduced levels of TNFα and part of the IFNγ(-/-) phenotype could be caused by reduced levels of IL6.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 expression in mice with intestinal or systemic infections of citrobacter rodentium.Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Feb;37(2):366-74. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.024240. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009. PMID: 18971315 Free PMC article.
-
Selective modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 and flavin monooxygenase 3 expression during citrobacter rodentium infection in severe combined immune-deficient mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Oct;40(10):1894-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.046557. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22745333 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic and renal cytochrome p450 gene regulation during citrobacter rodentium infection in wild-type and toll-like receptor 4 mutant mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Mar;34(3):354-60. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.007393. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16339354 Free PMC article.
-
Selective role for tumor necrosis factor-α, but not interleukin-1 or Kupffer cells, in down-regulation of CYP3A11 and CYP3A25 in livers of mice infected with a noninvasive intestinal pathogen.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Aug 1;82(3):312-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.04.016. Epub 2011 May 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21570957 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoform mRNAs during inflammation and infection in mouse liver and kidney.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Mar;34(3):351-3. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.007435. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16339353 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Altered inflammatory responses to Citrobacter rodentium infection, but not bacterial lipopolysaccharide, in mice lacking the Cyp4a10 or Cyp4a14 genes.Inflammation. 2014 Jun;37(3):893-907. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9809-6. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24413902 Free PMC article.
-
CCN1 expression in hepatocytes contributes to macrophage infiltration in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice.J Lipid Res. 2013 Jan;54(1):44-54. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M026013. Epub 2012 Oct 15. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23071295 Free PMC article.
-
Selective and cytokine-dependent regulation of hepatic transporters and bile acid homeostasis during infectious colitis in mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Apr;42(4):596-602. doi: 10.1124/dmd.113.055525. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014. PMID: 24378326 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation is a major regulator of drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters: Consequences for the personalization of drug treatment.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Nov;215:107627. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107627. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32659304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in COVID-19 Pathogenesis and Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 2;13:791922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.791922. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35185562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Razzak Z, Loyer P, Fautrel A, Gautier JC, Corcos L, Turlin B, Beaune P, Guillouzo A. Cytokines down-regulate expression of major cytochrome P-450 enzymes in adult human hepatocytes in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol. 1993;44:707–715. - PubMed
-
- Ashino T, Oguro T, Shioda S, Horai R, Asano M, Sekikawa K, Iwakura Y, Numazawa S, Yoshida T. Involvement of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α in CYP3A11 and 2C29 down-regulation by Bacillus Calmette-Guerin and lipopolysaccharide in mouse liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004;32:707–714. - PubMed
-
- Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ, David M, Andus T, Geiger T, Trullenque R, Fabra R, Heinrich PC. Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989;242:237–239. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

