Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus inhibits interleukin-4-mediated STAT6 phosphorylation to regulate apoptosis and maintain latency
- PMID: 20719954
- PMCID: PMC2953196
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01293-10
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus inhibits interleukin-4-mediated STAT6 phosphorylation to regulate apoptosis and maintain latency
Abstract
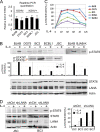
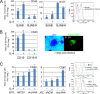
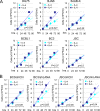
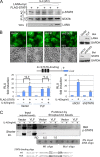
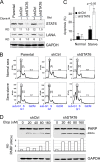
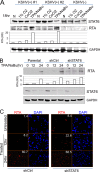
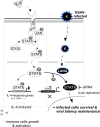
Cytokine-mediated JAK/STAT signaling controls numerous important biologic responses like immune function, cellular growth, and differentiation. Inappropriate activation of this signaling pathway is associated with a range of malignancies. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the infectious viral agent associated with Kaposi's sarcoma and may also contribute to B-cell disorders, which include primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) and multicentric Castleman's disease. However, regulation of cytokine-mediated lymphocytic immune response by KSHV is not fully understood. In this report, we demonstrate that KSHV suppresses the interleukin-4 (IL-4)-stimulated immune response of B-lymphocyte activation and cell proliferation. Moreover, we show that the latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) encoded by KSHV is essential for viral blocking of IL-4-induced signaling. LANA reduces phosphorylation of the signal transducers and activators of transcription 6 (STAT6) on Y-641 and concomitantly its DNA binding ability. Importantly, knockdown of endogenous STAT6 dramatically increases the sensitivity of PEL cells to low-serum stress or chemical-mediated cellular apoptosis and reactivation of KSHV from latent replication. Thus, these findings suggest that the IL-4/STAT6 signaling network is precisely controlled by KSHV for survival, maintenance of latency, and suppression of the host cytokine immune response of the virus-infected cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded LANA contributes to viral latent replication by activating phosphorylation of survivin.J Virol. 2014 Apr;88(8):4204-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03855-13. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24478433 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Localization and Cleavage of STAT6 Is Induced by Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus for Viral Latency.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 18;13(1):e1006124. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006124. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28099521 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive Activation of Interleukin-13/STAT6 Contributes to Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Related Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Proliferation and Survival.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10416-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01525-15. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26246572 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2-prostaglandin E2-eicosanoid receptor inflammatory axis: a key player in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus associated malignancies.Transl Res. 2013 Aug;162(2):77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23567332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV Genome Replication and Maintenance in Latency.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:299-320. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896673 Review.
Cited by
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded LANA contributes to viral latent replication by activating phosphorylation of survivin.J Virol. 2014 Apr;88(8):4204-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03855-13. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24478433 Free PMC article.
-
Egr-1 regulates RTA transcription through a cooperative involvement of transcriptional regulators.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 5;8(53):91425-91444. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20648. eCollection 2017 Oct 31. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29207655 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the STAT6 transcription factor in Jurkat T-cells by the herpesvirus saimiri Tip protein.J Gen Virol. 2012 Feb;93(Pt 2):330-340. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.036087-0. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22012462 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Cycle Regulatory Functions of the KSHV Oncoprotein LANA.Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 30;7:334. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00334. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27065950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The single RBP-Jkappa site within the LANA promoter is crucial for establishing Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency during primary infection.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(13):6148-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02608-10. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21507979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An, J., Y. Sun, and M. B. Rettig. 2004. Transcriptional coactivation of c-Jun by the KSHV-encoded LANA. Blood 103:222-228. - PubMed
-
- Antman, K., and Y. Chang. 2000. Kaposi's sarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 342:1027-1038. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, Y., G. M. Feldman, and G. Tosato. 2003. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood 101:1535-1542. - PubMed
-
- Aoudjehane, L., P. Podevin, O. Scatton, P. Jaffray, I. Dusanter-Fourt, G. Feldmann, P. P. Massault, L. Grira, A. Bringuier, B. Dousset, S. Chouzenoux, O. Soubrane, Y. Calmus, and F. Conti. 2007. Interleukin-4 induces human hepatocyte apoptosis through a Fas-independent pathway. FASEB J. 21:1433-1444. - PubMed
-
- Ballestas, M. E., P. A. Chatis, and K. M. Kaye. 1999. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 284:641-644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

