Constitutive endocytosis and recycling of NKCC2 in rat thick ascending limbs
- PMID: 20719977
- PMCID: PMC2980413
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00307.2010
Constitutive endocytosis and recycling of NKCC2 in rat thick ascending limbs
Abstract
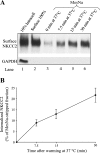
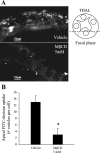
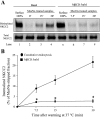
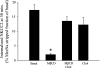
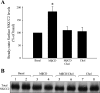
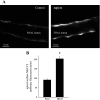
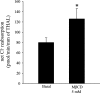
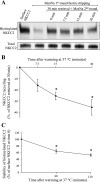
The Na-K-2Cl cotransporter (NKCC2) mediates NaCl absorption by the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop (THAL). Exocytosis and endocytosis regulates surface expression of most transporters. However, little is known about the mechanism of NKCC2 trafficking in the absence of stimulating hormones and whether this mechanism contributes to regulation of steady-state surface expression of apical NKCC2 in the THAL. We tested whether NKCC2 undergoes constitutive endocytosis that regulates steady-state surface NKCC2 and NaCl reabsorption in THALs. We measured steady-state surface NKCC2 levels and the rate of NKCC2 endocytosis by surface biotinylation and Western blot and confocal microscopy of isolated perfused rat THALs. We observed constitutive NKCC2 endocytosis over 30 min that averaged 21.5 ± 2.7% of the surface pool. We then tested whether methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD), a compound that inhibits endocytosis by chelating membrane cholesterol, blocked NKCC2 endocytic retrieval. We found that 30-min treatment with MβCD (5 mM) blocked NKCC2 endocytosis by 81% (P < 0.01). Blockade of endocytosis by MβCD induced accumulation of NKCC2 at the apical membrane as demonstrated by a 60 ± 16% (P < 0.05) increase in steady-state surface expression and enhanced apical surface NKCC2 immunostaining in isolated, perfused THALs. Acute treatment with MβCD did not change the total pool of NKCC2. MβCD did not affect NKCC2 trafficking when it was complexed with cholesterol before treatment. Inhibition endocytosis with MβCD enhanced NKCC2-dependent NaCl entry by 57 ± 16% (P < 0.05). Finally, we observed that a fraction of retrieved NKCC2 recycles back to the plasma membrane (36 ± 7%) over 30 min. We concluded that constitutive NKCC2 trafficking maintains steady-state surface NKCC2 and regulates NaCl reabsorption in THALs. These are the first data showing an increase in apical membrane NKCC2 in THALs by altering the rates of constitutive NKCC2 trafficking, rather than by stimulation of hormone-dependent signaling.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

